The retail landscape has transformed more in the past five years than it did in the previous fifty. Business leaders who once debated whether to build an online store now face a different question entirely: how do we stay competitive when customer expectations shift weekly, not yearly?
Traditional commerce platforms that once seemed cutting edge now struggle to keep pace. Retailers find themselves locked into rigid systems that take months to update, cost a fortune to maintain, and can’t integrate the latest tools their customers expect. This is where composable commerce enters the conversation as a fundamental shift in how retail technology gets built and deployed.
The retailers winning today share a common thread. They’ve moved beyond monolithic platforms toward modular architecture that gives them control, speed, and flexibility. This approach, known as composable commerce, represents the core of retail modernization and what industry analysts call Retail 4.0.
The Evolution of Retail: Setting the Stage for Retail 4.0
From Traditional to Tech-Driven Retail
Retail has evolved through distinct phases. Retail 1.0 centered on physical stores where face to face interactions drove sales. Retail 2.0 introduced eCommerce with basic digital catalogs. Retail 3.0 brought omnichannel experiences, connecting online and offline touchpoints.
Now we’re entering Retail 4.0, characterized by data driven decision making, artificial intelligence, and composable technology stacks. According to Oberlo’s global eCommerce analysis, global eCommerce sales reached $6.09 trillion in 2024 with a growth rate of 8.4%, and are projected to reach $8.09 trillion by 2028. The pandemic accelerated digital adoption by an estimated five years, permanently changing consumer expectations around convenience, personalization, and speed.
Defining Retail 4.0 in Today’s Context
Retail 4.0 means more than just having digital channels. It represents a fundamental shift toward intelligent, adaptive commerce ecosystems that leverage AI for predictive analytics, operate on cloud native infrastructure, and prioritize customer centric experiences.
The defining characteristic is flexibility. Retailers can no longer afford to wait 12 to 18 months for platform migrations. Market conditions change too quickly. This reality has forced retailers to rethink legacy architectures where monolithic systems create bottlenecks.
What Is Composable Commerce? A Framework for Retail Modernization
The Core Concept
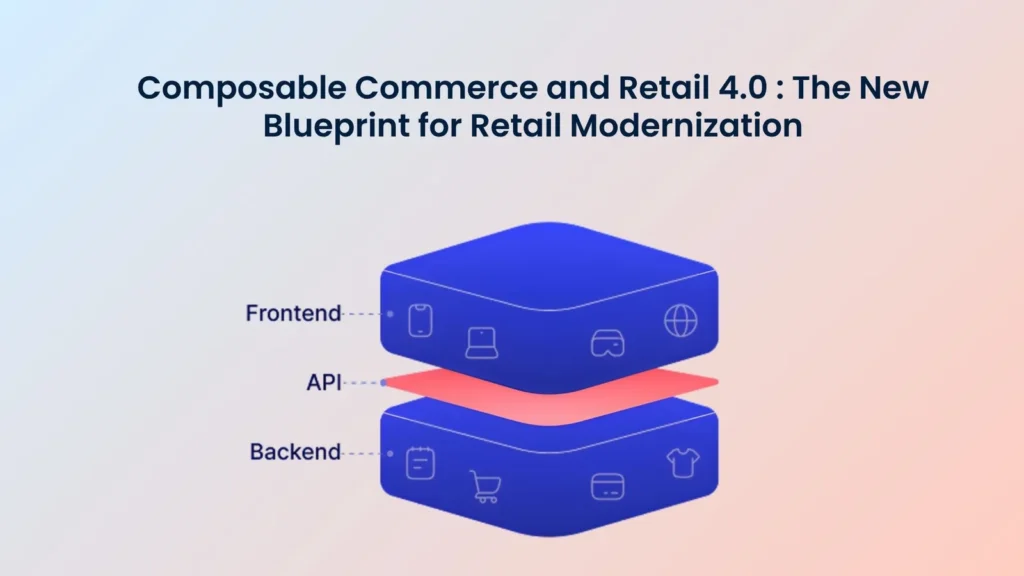
Composable commerce represents an architectural approach where businesses select, assemble, and orchestrate best of breed commerce components to create customized solutions. This retail modernization strategy moves beyond relying on a single vendor’s all in one platform, allowing retailers to build their technology stack from independent, interchangeable services.
Think of it like building with LEGO blocks rather than buying a pre assembled model. Each block serves a specific function and can be swapped without affecting the others. Your payment processing, content management, and inventory system all operate independently but communicate seamlessly through APIs.
Gartner research on composable enterprise applications predicts that 40% of enterprise applications will integrate task specific AI agents by the end of 2026, up from less than 5% in 2025. The analyst firm also notes that composable commerce adoption is growing rapidly among mid market and enterprise retailers as organizations seek greater agility and flexibility.
The Pillars of Composable Architecture
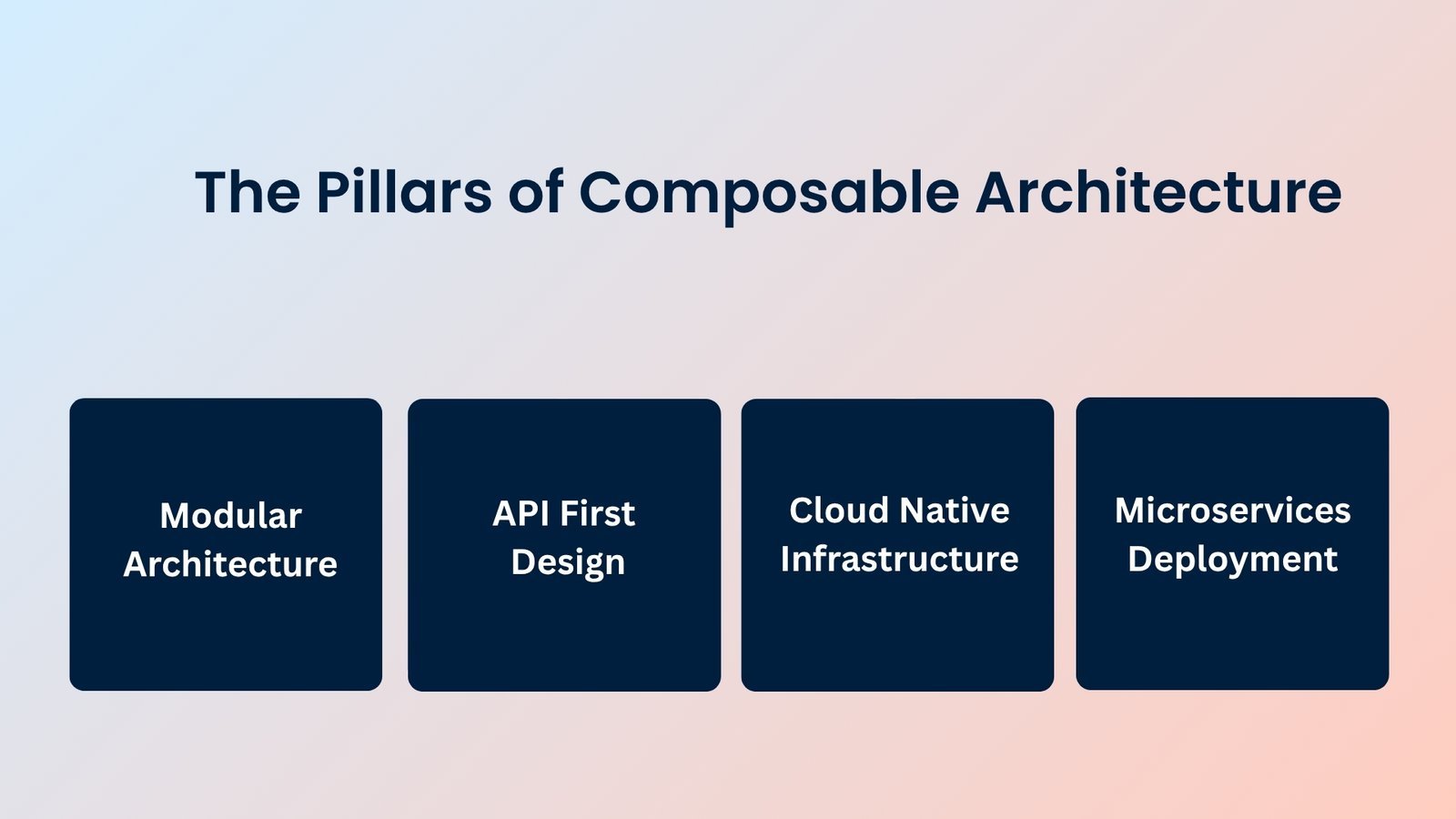
Four core principles define composable commerce:
Modular Architecture forms the foundation where each business capability exists as an independent, self contained module. Product catalogs, pricing engines, and order processing operate as separate services.
API First Design ensures all components communicate through well defined, standardized interfaces, allowing different services to exchange data without tight coupling.
Cloud Native Infrastructure provides the elasticity and reliability modern commerce demands, enabling services to scale automatically based on traffic.
Microservices and Independent Deployment enable teams to work on different capabilities simultaneously. Each service maintains its own release cycle, dramatically accelerating innovation.
Why Modularity Matters in Modern Retail
Modular architecture directly addresses the biggest constraint facing retailers: the inability to adapt quickly. When your composable commerce platform consists of independent modules, you gain unprecedented flexibility to experiment and respond to market changes, which is essential for successful retail modernization.
Consider a retailer wanting to test a new loyalty program. With a monolithic platform, this might take months. With composable commerce and modular architecture, the retailer simply integrates a specialized loyalty service through APIs and launches in weeks. This modularity enables agile retail where retailers can test hypotheses quickly and scale what works.
How Composable Commerce Is Powering Retail Digital Transformation
Agility and Faster Go to Market
Speed has become a competitive advantage. Composable systems compress timelines for launching new capabilities from months to weeks. Because services are loosely coupled, changes in one area don’t trigger cascading effects across the platform.
A major fashion retailer recently deployed a new buy now, pay later payment option in just three weeks using a composable approach. The same implementation on their previous monolithic platform had been estimated at four to six months.
Personalized and Omnichannel Customer Experiences
Composable commerce excels at delivering consistent, personalized experiences across channels. With data flowing freely between independent services through APIs, retailers can build unified customer profiles that inform every interaction.
According to McKinsey’s research on personalization, personalization can reduce customer acquisition costs by as much as 50%, lift revenues by 5% to 15%, and increase marketing ROI by 10% to 30%. Composable architectures make this level of personalization achievable without massive custom development projects.
Scalability, Flexibility, and Future Readiness
Perhaps the most strategic benefit is future readiness. When augmented reality shopping emerged, retailers with composable systems integrated AR services through APIs. Those on monolithic platforms either waited for their vendor to build the feature or faced complex custom development.
Market research indicates the global composable commerce platform market will grow from $4.8 billion in 2023 to approximately $14.5 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate of over 17%.
Key Benefits of Composable Commerce for Modern Retailers
Business Agility and Innovation
Composable commerce removes technical barriers that typically slow innovation in retail modernization initiatives. Product teams can experiment with visual search. Marketing can deploy personalized campaigns that adapt based on real time performance. Each team moves at their own pace, guided by business priorities rather than platform constraints.
Cost and Operational Efficiency
While composable commerce requires upfront planning, the long term cost structure often proves more favorable. License fees decrease because you’re not paying for bundled functionality you don’t use. Development costs drop because changes are more isolated and less risky.
Operational efficiency improves through selective scaling. If your search functionality needs more capacity during peak traffic but your checkout doesn’t, you scale only what’s necessary.
Reduced Vendor Lock In and Technical Debt
Monolithic platforms create dependency on a single vendor’s roadmap. Composable commerce reverses this dynamic. You select best of breed solutions for each capability. If a better option emerges, you swap that component while keeping everything else intact.
Technical debt also accumulates more slowly. In monolithic systems, customizations pile up over time. With composable architecture, technical debt remains isolated to specific services.
Enhanced Customer Experience
All these technical benefits ultimately serve one purpose: delivering better customer experiences. Customers experience faster page loads when systems scale independently. They encounter fewer errors when changes to one service don’t destabilize others.
The seamless omnichannel experiences that customers demand become achievable. A customer can start shopping on mobile, receive personalized recommendations via email, and complete their purchase in store with all preferences intact.
Real World Proof: How Retail Leaders Are Winning with Composable Commerce
Case Study 1: Global Sports Brand Transforms Digital Commerce with Composable Architecture
A leading global sports and athletic wear brand faced significant challenges with their monolithic commerce platform. The legacy system made it difficult to deliver personalized experiences across multiple brands, regions, and customer touchpoints. Every update required extensive coordination, and launching new features took months of development and testing cycles.
The brand decided to rebuild their entire digital commerce infrastructure using composable principles. They decomposed their monolithic platform into independent microservices, implementing a headless architecture that separated the frontend presentation layer from backend commerce logic. The transformation included integrating specialized services for product information management, personalization engines, payment processing, and customer data platforms.
Results achieved:
- Nike’s fiscal 2026 Q1 showed strategic transformation with wholesale growing 5% while repositioning their digital business for long term growth
- Time to market for new features reduced from 4 to 6 months to 2 to 3 weeks through composable architecture
- Running business segment grew over 20% in recent quarters, demonstrating effective sport focused innovation
- Ability to run over 100 personalized campaigns simultaneously across different customer segments
- Successfully scaled infrastructure to handle peak traffic during product launches
The modular architecture enabled them to experiment rapidly with new customer experiences. They could test different product discovery mechanisms, checkout flows, and personalization strategies across specific customer segments without risking the entire platform. The composable approach also facilitated their international expansion, allowing regional teams to customize experiences for local markets while maintaining global consistency in core commerce capabilities.
According to Nike’s fiscal 2026 Q1 earnings report, their digital transformation and composable architecture have been instrumental in achieving their strategic goal of creating deeper, more direct relationships with consumers. The flexibility of composable commerce allowed them to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and consumer behaviors.
Case Study 2: Furniture Retail Giant Achieves Global Scale with Composable Commerce
A multinational furniture and home goods retailer with operations in over 50 countries struggled with their global commerce infrastructure. Their existing system couldn’t efficiently handle the complexity of managing thousands of products, multiple currencies, diverse payment methods, and varying regulatory requirements across different markets. Local teams had limited autonomy to optimize experiences for their specific customer base, while the central technology team was overwhelmed trying to manage a rigid, monolithic platform.
The retailer embarked on a multi year transformation to adopt composable commerce principles. They implemented a modular architecture that standardized core services like product information management, inventory visibility, and order orchestration globally while enabling regional flexibility for customer facing experiences. The API first approach allowed them to integrate best of breed solutions for specific capabilities while maintaining overall system coherence.
Transformation outcomes:
- Unified commerce operations across 50+ countries while maintaining local market flexibility
- Reduced platform operational costs by 35% through selective scaling and optimized resource utilization
- Improved online conversion rates by 25% through better personalization and localized experiences
- Decreased time to launch new markets from 12-18 months to 3-4 months
- Enhanced inventory visibility across channels, reducing stockouts by 20%
The composable approach proved particularly valuable during the pandemic when the retailer needed to rapidly deploy new fulfillment capabilities like curbside pickup and same day delivery. What would have taken 8-12 months on their legacy platform was accomplished in weeks by integrating specialized fulfillment services through APIs.
Regional teams gained the autonomy to optimize payment methods, shipping options, and promotional strategies for their local markets without waiting for central IT approval or global rollouts. This localization capability, combined with global consistency in product data and inventory management, created a powerful balance that drove both customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
According to Retail Dive, the furniture retailer’s digital transformation has become a model for other global retailers navigating the complexity of composable commerce adoption at scale. Their phased implementation approach, starting with non customer facing services before moving to customer touchpoints, minimized risk while building organizational competence with the new architecture.
Industry Examples and Adoption Trends
Beyond these detailed case studies, composable commerce adoption is accelerating across retail categories. Fashion brands are using modular architecture to launch seasonal collections faster. Grocery retailers are integrating specialized delivery and fulfillment services to compete with digital native players. Electronics retailers are deploying augmented reality try before you buy experiences through composable integrations.
Retailers typically report 40% to 60% reduction in time to deploy new features after transitioning to composable architectures. More importantly, they gain the strategic flexibility to adapt as market conditions evolve, customer expectations change, and new technologies emerge.
Lessons for Emerging Retailers
Composable commerce isn’t just for enterprise retailers with massive technology budgets. Small and medium sized retailers can adopt composable principles gradually as part of their retail modernization journey, starting with areas of greatest business impact.
Many successful journeys begin with headless content management, allowing retailers to update their frontend experiences without touching backend systems. Others start by replacing payment processing or search functionality with specialized services that deliver immediate customer experience improvements.
The key lesson from these case studies is to start with clear business objectives rather than technology for its own sake. Identify the capabilities causing the most friction in your current platform. Determine which limitations most directly impact revenue or customer satisfaction. Then prioritize those areas for initial composable implementations.
Transitioning to Composable Commerce: A Step by Step Roadmap
Step 1: Evaluate Existing Infrastructure
Begin by thoroughly assessing your current commerce technology. Document the capabilities you have, their interdependencies, and specific pain points. Identify which systems are causing the most significant bottlenecks.
This evaluation should involve both technical teams and business stakeholders to map out the architecture and articulate which capabilities most directly impact strategic objectives.
Step 2: Define Strategic Goals
Clarity on outcomes guides effective decision making. Are you primarily seeking faster time to market? Do you need better scalability? Is international expansion requiring more flexible localization?
Document goals with measurable targets. Instead of “improve agility,” aim for “reduce time to deploy new payment methods from 12 weeks to 3 weeks.”
Step 3: Implement in Phases
Successful composable transformations happen incrementally. Many retailers begin with their content management system, moving to a headless CMS. Others start with specialized services like search or payment processing.
Each phase should follow a consistent pattern: select the service, integrate through APIs, test thoroughly, deploy to a limited audience, measure results, and scale gradually.
Step 4: Align People, Process, and Technology
Technology transformation requires corresponding changes in team structure. Composable commerce enables cross functional teams to work more independently, but this autonomy requires clear governance.
Successful retailers typically establish centers of excellence for key capabilities like API management and service orchestration. Change management studies indicate that transformations with strong executive sponsorship have success rates over 70%, compared to less than 30% for those lacking these elements.
Transform with RBM Software: Enabling the Future of Retail
RBM’s Expertise in Composable and Modular Architecture
RBM Software has built deep expertise in retail digital transformation through hands on work with leading brands. Our team brings practical experience in API management, microservices architecture, headless commerce implementations, and cloud native deployment.
Our work with major retailers like Restoration Hardware and Big Lots demonstrates our capability to handle enterprise scale commerce transformations. These engagements involved modernizing legacy systems, implementing modular architectures, and enabling omnichannel capabilities that drive revenue growth.
Tailored Solutions for Agile Retail
RBM Software understands that every retailer’s journey toward composable commerce is unique. We work closely with your team to understand your specific challenges and strategic priorities.
Our solutions enable faster go to market for new capabilities while ensuring seamless scalability. Clients typically see significant improvements: time to market decreases by 50% or more, platform incidents drop substantially, and customer satisfaction scores improve.
Why Partnering with RBM Software Delivers Results
Retail modernization requires both technical excellence and business insight. RBM Software brings both to every engagement.
As an experienced digital product engineering services company, we focus relentlessly on outcomes, measuring success by whether solutions drive revenue growth, reduce costs, and enable strategic flexibility.
Ready to empower your retail modernization journey? Let RBM Software’s composable commerce solutions provide the flexibility, speed, and innovation your business needs to compete effectively in the Retail 4.0 era.
Conclusion: The Future Belongs to the Composable Retailers
Composable commerce represents more than a technology trend. It’s a fundamental shift in how retailers build digital infrastructure for successful retail modernization. The flexibility, speed, and future readiness it enables are essential capabilities for competing in markets where customer expectations evolve constantly.
The retailers thriving today have embraced modular architecture that enables rapid experimentation. They’ve adopted API first principles that facilitate integration. They’ve built organizational capabilities to leverage composable systems effectively.
The transition requires investment and commitment, but the alternative carries greater risk. Remaining on rigid platforms means watching more agile competitors capture market share and struggling to meet evolving customer expectations.
Your retail modernization journey starts with understanding where composable commerce can drive the most value for your specific situation. Connect with RBM Software to explore how composable commerce can transform your retail operations. Let’s discuss your challenges and create a modernization roadmap tailored to your business.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
1. What is the main difference between composable commerce and traditional eCommerce platforms?
Traditional eCommerce platforms bundle all functionality into a single system where components are tightly coupled. Composable commerce uses modular architecture where each capability exists as an independent service connected through APIs. This retail modernization approach means you can upgrade or replace individual components without affecting the entire system, giving you greater flexibility and faster time to market.
2. How long does it typically take to transition to a composable commerce architecture?
The timeline varies based on your current infrastructure and approach. Most retailers adopt composable commerce principles gradually over 12 to 24 months rather than attempting a complete replacement. You might start by implementing a headless CMS in just a few weeks, then progressively modernize other components. This phased retail modernization approach reduces risk while delivering incremental value.
3. Is composable commerce only suitable for large enterprise retailers?
Not at all. While enterprise retailers were early adopters, composable commerce is increasingly accessible to mid market and smaller retailers. Many specialized commerce services now offer pricing models that work for businesses of various sizes. The key is starting with the capabilities that deliver the most value rather than rebuilding everything at once.
4. What are the typical cost implications of moving to composable commerce?
Initial costs include assessment, planning, and integration work. However, long term total cost of ownership frequently decreases. You eliminate paying for bundled features you don’t use and gain efficiency through selective scaling. Most retailers see positive ROI within 18 to 24 months through reduced platform fees, lower development costs, and revenue growth from improved capabilities.
5. How does composable commerce improve customer experience?
Composable architecture enables several improvements. You can deploy personalization engines that analyze behavior in real time across all channels. You can integrate best of breed services for search and recommendations. You can update frontend experiences without backend changes, allowing faster optimization. Most importantly, you can quickly adopt emerging technologies that customers expect.