Implementing an Ecommerce Chatbot : The Key to Smarter Online Selling


In today’s data-driven organizations, enterprise search security systems are the backbone of decision-making. They enable employees to quickly find critical information across multiple platforms, databases, and applications. However, with this convenience comes significant risk. Unsecured enterprise search security systems can expose sensitive corporate data, customer information, and intellectual property to cybercriminals or internal misuse.
According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025, the global average cost of a data breach is $4.44 million, while U.S. organizations face an average cost of $10.22 million per incident — underscoring the widening gap in breach impact across geographies.
A Harvard Business Review (2025) analysis further notes that over 80 percent of enterprise cloud breaches originate from misconfigured permissions or weak identity controls, directly linking enterprise search exposure to cloud security posture.
Meanwhile, Okta’s 2025 Secure Sign-In Trends Report indicates that 91 percent of global enterprises now enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for privileged accounts, yet enterprise search applications remain among the least protected with MFA coverage still below 60 percent.
Here is a snapshot of common enterprise search security risks:
| Risk Type | Impact on Business | Likelihood (1-5) | Example Scenario |
| Unauthorized Access | Data leak, intellectual property loss | 5 | Employee shares sensitive research data without clearance |
| Weak Authentication Methods | Credential theft, system intrusion | 4 | Password-only login exploited by hackers |
| Poor Data Masking | Exposure of confidential customer info | 3 | Customer emails visible in search results |
| Insider Threats | Sabotage or unintentional errors | 3 | Internal user accidentally deletes critical documents |
Securing enterprise search systems is not just an IT requirement—it is a business imperative. Organizations that implement secure authentication methods, data masking in search, and continuous monitoring can prevent data breaches and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
The cost of ignoring enterprise search security far exceeds the investment required to implement effective safeguards. Protecting your enterprise systems today safeguards your company’s reputation, revenue, and operational efficiency.
Enterprise search systems are designed to help organizations retrieve information efficiently from multiple internal and external sources. Unlike consumer search engines, these systems are tailored for corporate environments, indexing documents, emails, databases, and applications to ensure employees can access the right information at the right time
An enterprise search system is a technology solution that allows users to search across the organization’s data repositories using keywords, filters, and metadata. These systems integrate with multiple platforms, including content management systems, customer relationship management systems, and cloud storage, to provide a unified search experience.
Modern enterprise search systems enforce document-level security (DLS) and field-level security (FLS), ensuring that users only see documents and data fields they’re authorized to access. Advanced controls such as Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) enable fine-grained policy enforcement based on user roles, data sensitivity, and contextual factors (e.g., device, location).
Data confidentiality is further protected through tokenization of sensitive identifiers and TLS 1.3 for encrypted data transmission between servers and endpoints.
How RBM Implements This: At RBM, we architect enterprise search security deployments with built-in DLS/FLS configurations, ABAC policy layers, and end-to-end encryption using TLS 1.3 and AES-256. Our engineers also implement customer-managed key (CMK) and Hardware Security Module (HSM) integrations for enterprises that require heightened control over encryption keys and audit traceability.
Enterprise search systems enable faster and more informed decision-making by providing:
For instance, a sales team can instantly retrieve customer interaction history across CRM systems, marketing reports, and emails to make strategic proposals. Similarly, a research and development team can find technical specifications and prior project documents without delays, speeding up product development cycles.
A well-secured enterprise search environment must include security trimming, where users only view search results for data they have permission to access, preventing inadvertent disclosure through indexing. Additionally, integrating policy-as-code frameworks and User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) allows continuous monitoring of access anomalies, providing early warning of insider or credential-based threats.
Enterprise search systems consolidate vast amounts of sensitive information, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals and potential failure points within organizations. Understanding these threats is crucial for business leaders making informed security decisions.
Data breaches represent the most significant threat to enterprise search systems. Unauthorized users—whether external hackers or internal personnel can access confidential business data, resulting in financial loss and reputational damage.
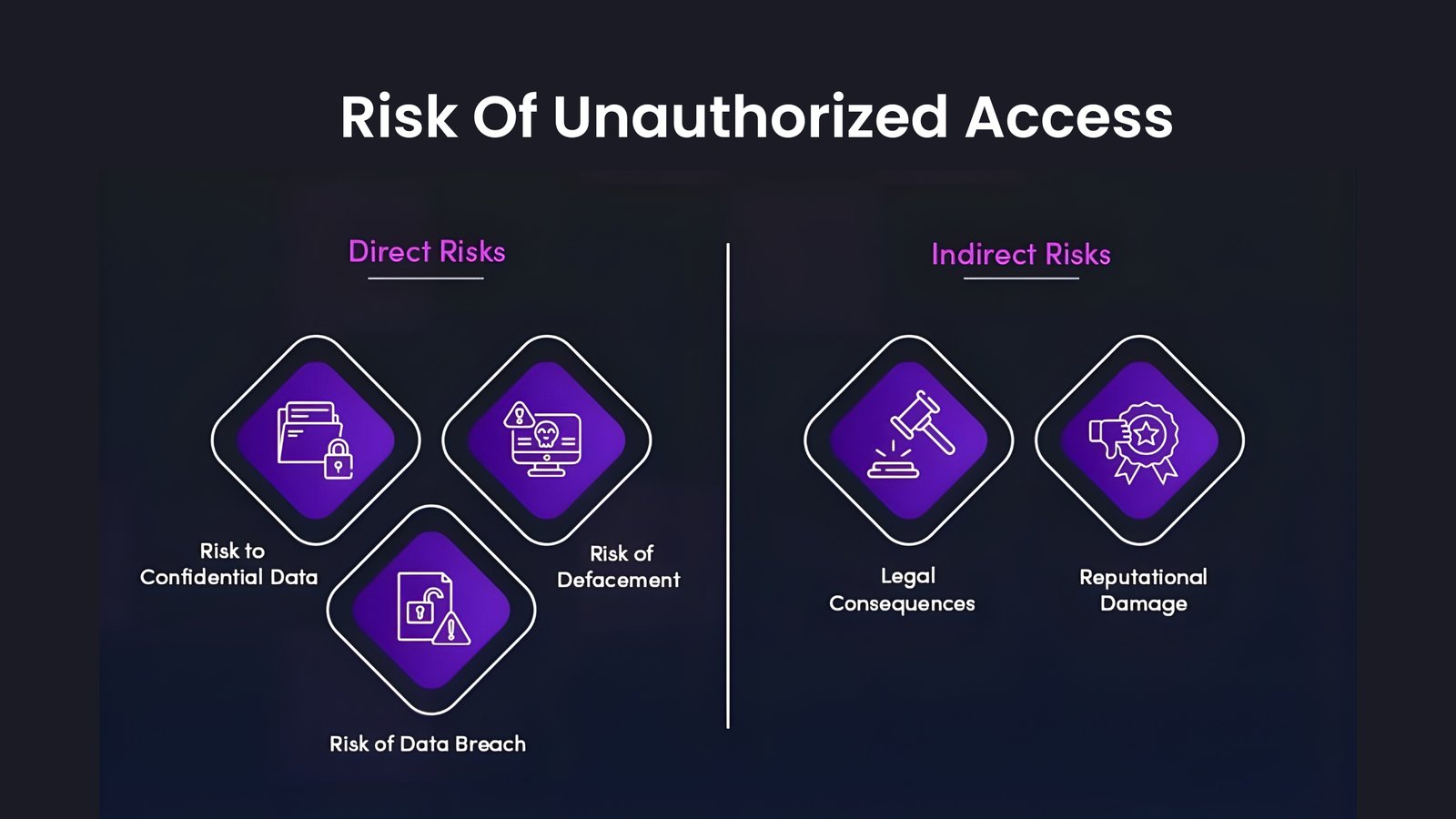
Unauthorized access often stems from insufficient access controls or misconfigured document- and field-level security (DLS/FLS), allowing users to see data beyond their clearance. Implementing attribute-based access control (ABAC) and regular permission reviews greatly limits these breaches.
How RBM Implements This: RBM hardens enterprise-search deployments through security trimming, granular ABAC policies, and AES-256 encryption with TLS 1.3 transport protection, ensuring data remains restricted and unreadable outside approved access scopes.
| Threat | Frequency (%) | Average Cost (USD) | Potential Impact |
| External Hacking | 35 | 4,500,000 | Intellectual property theft, customer data exposure |
| Internal Breach | 25 | 3,200,000 | Sabotage, accidental exposure of sensitive data |
| Credential Theft | 20 | 2,800,000 | Unauthorized system access, operational disruption |
| Misconfigured Access | 15 | 1,500,000 | Employees accessing data beyond their role |
| Phishing & Social Engineering | 5 | 1,200,000 | Compromise of authentication methods |
Outdated authentication methods leave enterprise systems vulnerable. Password-only logins or shared credentials make unauthorized access easier. Secure authentication methods—multi-factor authentication, role-based access controls, and token-based systems are essential for risk reduction.
Advanced deployments use dynamic data masking (DDM) and tokenization to replace regulated data fields (such as PII or financial IDs) with context-aware surrogates. When combined with customer-managed keys (CMK) or hardware security modules (HSMs), even privileged administrators cannot decrypt data outside approved workflows.
Not all risks originate outside the organization. Insider threats, intentional or accidental—compromise enterprise search security. Examples include employees mistakenly uploading sensitive documents to shared folders or intentionally leaking proprietary data. Training, monitoring, and clear role-based access policies help mitigate these risks.
The cost of neglecting enterprise search security is tangible. Organizations experiencing breaches in enterprise systems spend approximately 2.5 times more on remediation and legal costs than they would on implementing robust security measures upfront.
Securing enterprise search systems is not a one-time activity. It requires a multi-layered approach that combines technology, processes, and people. Business leaders must understand the pillars of enterprise search security to implement a strategy that prevents breaches while maintaining operational efficiency.
Authentication is the first line of defense for enterprise search systems. Strong authentication ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive information. Effective strategies include:
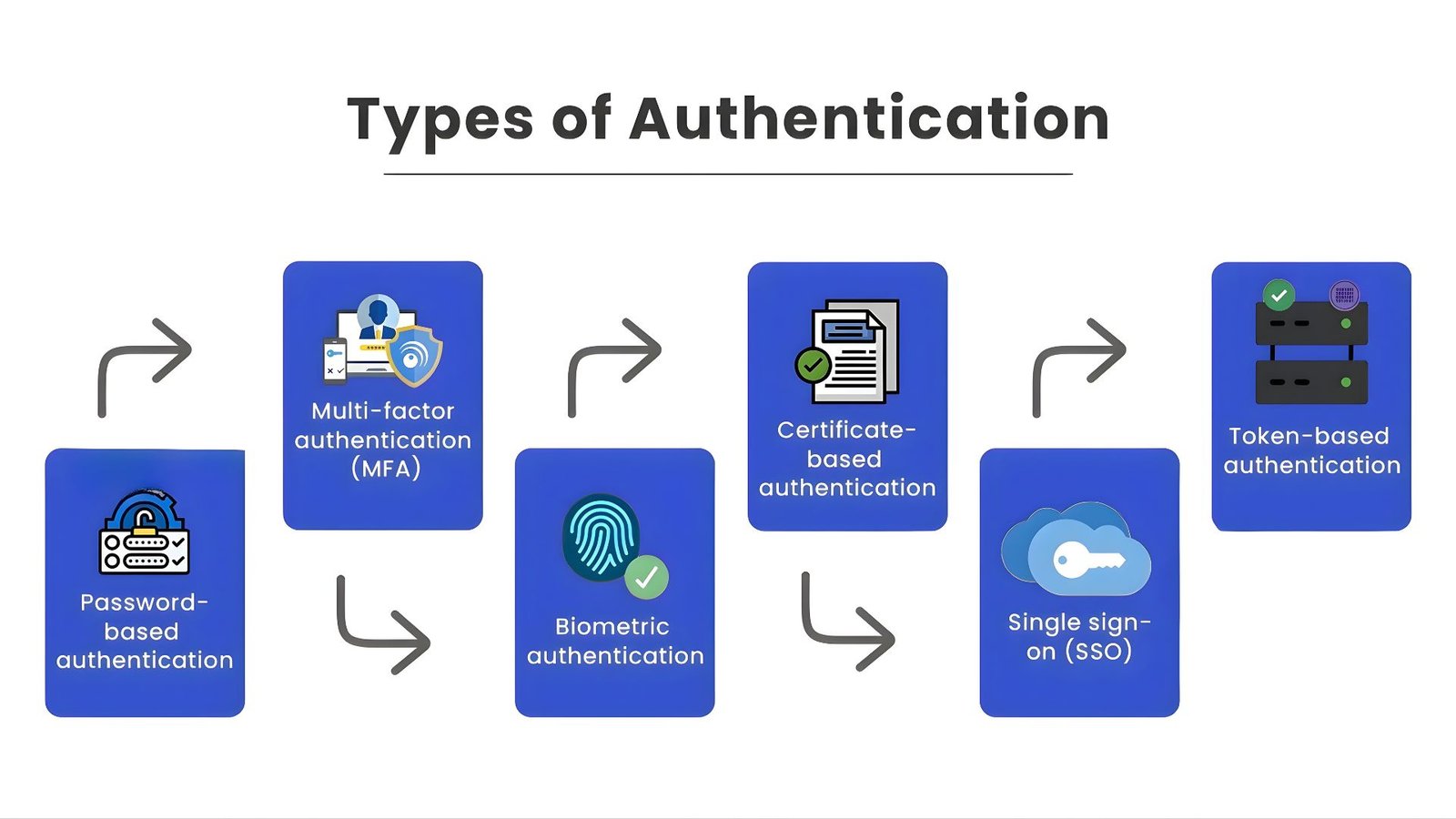
Modern enterprise environments extend these methods using Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) for finer policy enforcement and integrate TLS 1.3 for encrypted sessions between clients and servers. According to IBM’s 2025 data, enterprises that deploy strong identity controls reduce credential-related breach costs by up to 43%.
How RBM Implements This: RBM configures layered authentication models using MFA, SSO, and ABAC policies aligned with organizational IAM systems. This not only enhances protection but also improves audit readiness and reduces Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) for identity-based incidents.
Data masking is a critical safeguard that ensures sensitive information is not exposed during search queries. There are several techniques organizations can use:
Advanced implementations combine DDM with tokenization and Customer-Managed Keys (CMK) to ensure end-to-end encryption control. This approach protects regulated data under compliance standards such as GDPR and HIPAA while reducing the cost of audits and compliance penalties by up to 25%, according to Gartner’s enterprise security benchmarking.
For example, in a healthcare organization, patient names and medical record numbers can be masked for staff not directly involved in patient care. This reduces the risk of accidental exposure while still allowing employees to perform their tasks efficiently.
Encryption protects enterprise data both when it is stored and when it moves across networks. Without encryption, attackers can intercept sensitive information, including financial records or confidential reports. Best practices include AES-256 for data at rest, TLS 1.3 for data in transit, and integration with HSMs or CMK systems for key management. These controls align with NIST SP 800-57 and ISO/IEC 27001 standards for enterprise-grade encryption assurance.
How RBM Implements This: RBM deploys centralized key orchestration through HSM-backed vaults, ensuring encryption keys never leave customer-controlled environments. This enhances compliance with data residency and sovereignty requirements across multi-cloud systems.
Continuous monitoring is essential to detect unusual activity in enterprise search systems. Solutions include:
When integrated with User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) and SIEM systems, continuous monitoring reduces Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) by as much as 50%, directly improving operational resilience and limiting financial exposure during incidents.
Monitoring not only prevents breaches but also helps organizations respond quickly when a threat is detected.
Enterprise search security is closely tied to regulatory compliance. Depending on the industry, organizations may need to adhere to standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001. Compliance requires implementing secure authentication methods, data masking, and audit trails to demonstrate that data is handled responsibly and securely.
Securing enterprise search systems is more than deploying tools. It requires a structured approach that combines assessment, implementation, and continuous improvement. Business leaders must align security initiatives with operational goals to maximize both protection and efficiency.
Technology alone cannot secure enterprise search. Organizations need teams that understand security risks and act accordingly.
This requires:
Investing in enterprise search security is financially justifiable. Consider the table below, comparing the cost of implementing security measures versus the potential cost of a data breach:
| Investment Area | Estimated Cost (USD) | Potential Breach Cost (USD) | ROI Justification |
| Multi-Factor Authentication | 50,000 | 4,500,000 | Prevents credential theft and unauthorized access |
| Data Masking Integration | 40,000 | 3,200,000 | Reduces exposure of sensitive information |
| Continuous Monitoring Systems | 70,000 | 2,800,000 | Enables early threat detection and mitigation |
| Security Audits & Compliance | 30,000 | 1,500,000 | Ensures regulatory compliance and avoids fines |
This framework demonstrates that a proactive approach to enterprise search security not only mitigates risk but also provides a strong return on investment by avoiding potentially catastrophic financial and reputational losses.
Understanding the practical application of enterprise search security measures can provide valuable insights for business leaders. Below are real-world examples from various industries demonstrating how organizations have successfully implemented security measures to protect their enterprise search systems.
Cisco, a global leader in networking and cybersecurity solutions, faced challenges in providing efficient and secure search capabilities for its vast repository of technical support content. To address this, Cisco partnered with Elastic to enhance its enterprise search infrastructure.
Challenges:
Solution Implemented:
Outcome:
SAP, a global leader in enterprise software, aimed to unify its observability strategy to enhance security and performance monitoring across its vast cloud ecosystem. By leveraging OpenSearch and OpenTelemetry, SAP achieved its objectives.
Challenges:
Solution Implemented:
Outcome:
A global retail conglomerate managing millions of customer profiles implemented dynamic data masking and role-based access within its enterprise-search platform. The initiative reduced personally identifiable information (PII) visibility in search results by 95 percent, meeting GDPR data-minimization requirements.
How RBM Helped: RBM deployed Elastic with fine-grained field-level security and policy-as-code enforcement. Dashboards tracked data-exposure metrics, showing a measurable reduction in PII access events within the first quarter.
A healthcare network needed to ensure its enterprise-search tool complied with HIPAA while supporting doctors and administrators in querying patient information. By integrating ABAC, data masking, and tokenization controls, the organization achieved zero audit findings during external compliance reviews.
How RBM Helped : RBM integrated dynamic masking logic within OpenSearch queries using policy-as-code modules. The deployment enabled controlled access to patient identifiers without interrupting clinical workflows.
A multinational financial-services firm sought to reduce insider-threat risk within its document and records-search platform. By connecting search logs to a UEBA-driven SIEM, the company improved insider-threat detection by 40 percent, cutting response times and limiting unauthorized data exports.
How RBM Helped: RBM implemented an OpenSearch-SIEM integration pipeline with real-time anomaly detection and alert triage automation, allowing the firm to visualize user-behavior anomalies through unified dashboards.
Across these sectors, deploying multi-layered enterprise-search security controls delivered consistent outcomes:
These case studies illustrate the practical application of enterprise search security measures across various industries. By implementing robust security protocols, organizations can enhance the efficiency and safety of their enterprise search systems.
Implementing enterprise search security is a continuous process. Organizations that follow best practices not only reduce risk but also improve efficiency, compliance, and user trust.
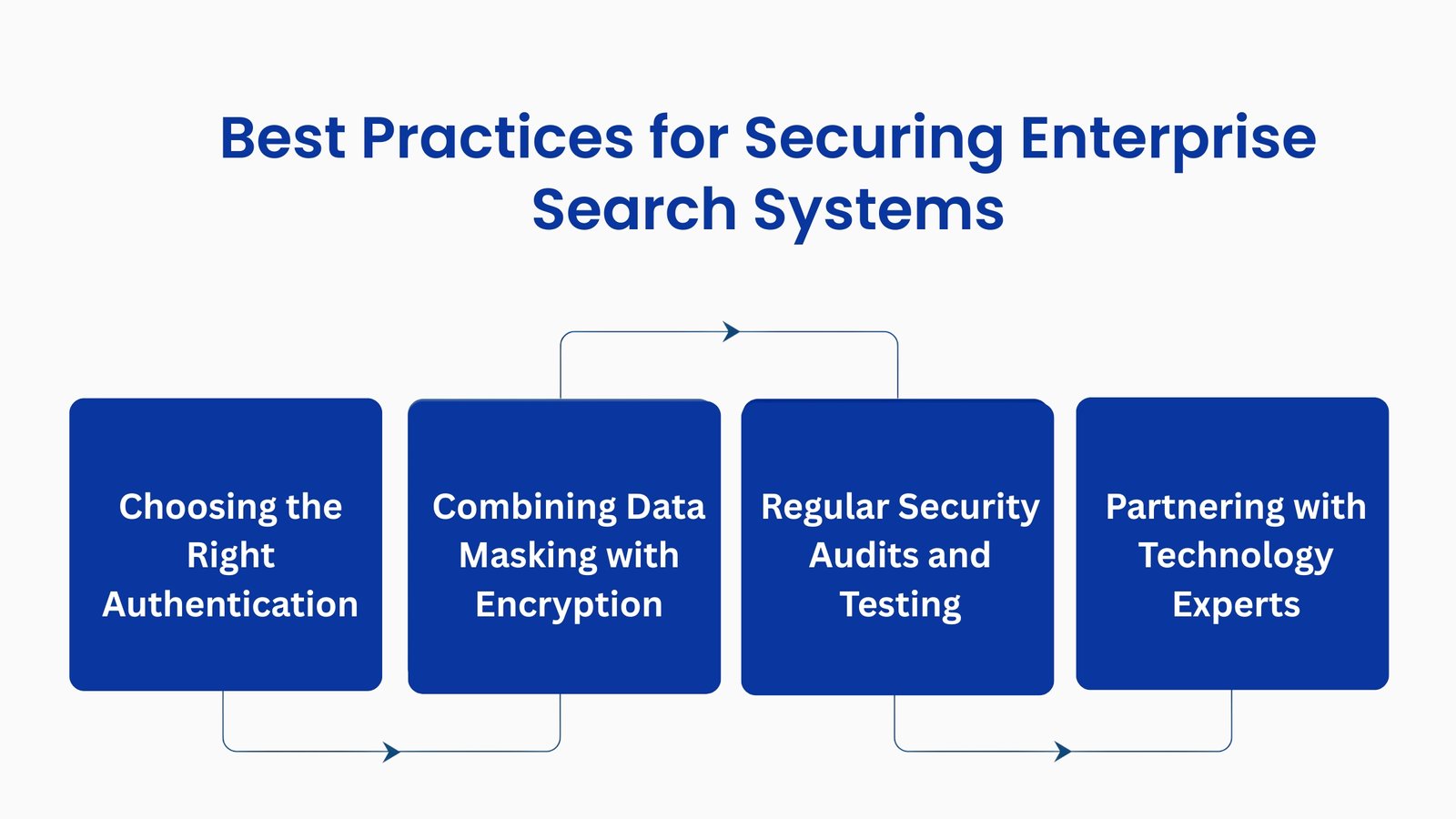
Selecting the correct authentication approach is critical for protecting enterprise systems. Multi-factor authentication, token-based access, and role-based permissions should be implemented based on the organization’s structure and sensitivity of data. For example, financial departments handling sensitive transactions may require biometric verification, while marketing teams may use token-based access for temporary projects. Regularly reviewing authentication policies ensures that they evolve with changing threats.
Data masking and encryption are complementary measures. While encryption protects data during storage and transmission, masking ensures that sensitive information is hidden from unauthorized users within the system. Organizations should implement dynamic masking for real-time queries and static masking for testing environments. This dual-layered approach minimizes exposure without affecting operational efficiency.
Continuous evaluation of enterprise search systems is essential. Conducting periodic security audits and penetration testing helps identify vulnerabilities before they are exploited. These audits should include testing of authentication methods, data masking protocols, encryption measures, and monitoring tools. Documenting audit findings ensures that remediation steps are tracked and enforced.
Even the most sophisticated internal teams can benefit from external expertise. Partnering with technology experts allows organizations to implement the latest security solutions, stay compliant with regulations, and adopt innovative approaches such as AI-driven threat detection. Experts can also provide training and guidance, reducing the risk of human error, which remains a major contributor to breaches
Enterprise search security is evolving rapidly. Emerging technologies, particularly artificial intelligence, are reshaping how organizations protect their data while maintaining search efficiency.
AI enables proactive threat detection by analyzing patterns of user behavior and system activity. Machine learning algorithms can identify anomalies that may indicate an attempted breach, such as unusual access times or repeated failed login attempts. This predictive capability allows organizations to respond immediately, reducing the likelihood of data loss.
Automation is transforming how sensitive information is protected. AI-powered data masking solutions can dynamically identify sensitive fields and apply masking rules in real-time, minimizing human intervention. This ensures that even complex and high-volume enterprise search queries remain secure without slowing down business operations.
Predictive security uses historical data and AI models to anticipate potential vulnerabilities or attacks before they occur. For enterprise search systems, this could mean preemptively restricting access to certain data during unusual activity patterns or alerting security teams about potential internal threats. Organizations that adopt predictive security gain a significant advantage by preventing breaches rather than reacting to them.
Securing enterprise search systems is no longer optional for modern organizations. As data volumes grow and enterprises increasingly rely on search capabilities for business-critical decisions, risks such as unauthorized access, weak authentication methods, and insufficient data masking create serious vulnerabilities.
Organizations adopting a multi-layered defense—MFA, dynamic masking, encryption, continuous monitoring, and predictive analytics—report up to 45 percent lower breach-related costs and faster compliance validation cycles.
RBM Soft specializes in enterprise-grade search solutions with security at the core. Our approach combines proven technology implementation with strategic business consulting to deliver measurable results.
Our Enterprise Search Security Services:
Why Organizations Choose RBM Soft:
Organizations that partner with RBM Soft gain more than security—they gain confidence that their enterprise systems protect what matters most.
Ready to secure your enterprise search system? Contact RBM Soft to schedule a security assessment and learn how we can help you implement comprehensive protection strategies.
Enterprise search security involves protecting sensitive information indexed and accessible through an organization’s search system. It matters because unprotected search systems can expose confidential data, lead to regulatory violations, and create opportunities for data breaches.
Data masking hides sensitive information from users who do not have the required permissions. It ensures that employees or external users can access the data they need without exposing personally identifiable information, financial records, or intellectual property.
The most effective methods include multi-factor authentication, role-based access controls, and token-based authentication. These methods prevent unauthorized access, reduce credential theft risks, and allow fine-grained control over who can view sensitive information.
While it cannot eliminate all risks, enterprise search security minimizes insider threats by implementing role-based access, monitoring user behavior, and applying data masking. Continuous audits and alerts help detect suspicious activity early.
Organizations that fail to secure enterprise search systems risk violations of regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO standards. Non-compliance can result in fines, legal penalties, and reputational damage.
Data breaches in enterprise systems can cost millions of dollars, including remediation, legal fees, and operational disruption. Investing in security measures like authentication, encryption, and data masking is often a fraction of the potential breach cost and provides strong ROI.
Enterprise search systems should be audited at least annually, with additional reviews whenever significant system updates or role changes occur. Critical systems may require quarterly audits and ongoing monitoring to maintain robust security.
AI enhances threat detection by analyzing patterns and predicting potential breaches. It also enables automated data masking, anomaly detection, and predictive security measures, allowing organizations to proactively protect sensitive information.