The choice of a front-end framework has become one of the most important decisions in modern web development. It affects how fast applications load, how easily they scale, how well they perform in search rankings, and how productive teams can be when building features. For companies investing in headless commerce and digital platforms, the framework decision directly impacts business results.
Over the years, JavaScript front-end framework have reshaped the way applications are built. What started with jQuery’s quick fixes moved into more structured approaches with Angular, then into the component-driven flexibility of React and Vue. Today, the landscape includes not only these core frameworks but also meta-frameworks like Next.js, Nuxt, and SvelteKit that add layers of optimization and server-side rendering.
React, Vue, and Angular remain the most widely adopted choices, each backed by strong communities and ecosystems. The challenge for businesses is not deciding which front-end framework is most popular, but which one best supports their goals in performance optimization, scalability, and integration with headless commerce solutions.
This blog explores the strengths and trade-offs of each front-end framework, compares their performance in enterprise contexts, and highlights real-world case studies to show what the right choice can deliver in practice. But first, let’s understand why this decision matters so much for enterprise success.
Why Front-End Framework Choice Matters for Enterprises
For enterprises, picking a front-end framework is more than a technical decision. It directly influences how digital platforms perform, scale, and support growth. The framework you choose becomes the foundation for customer experiences, and it can either accelerate or slow down digital transformation.
Scalability across teams and products
- Large organizations often manage multiple digital products built by distributed teams
- A framework with strong architecture and reliable patterns keeps projects consistent as they scale
- Angular offers structure out of the box, appealing to enterprises running complex applications across different teams
SEO performance and search visibility
- Every second of load time impacts search rankings and conversions in competitive markets
- Frameworks like React with Next.js or Vue with Nuxt support server-side rendering
- This improves Core Web Vitals and boosts SEO – particularly valuable for headless commerce where organic visibility drives sales
Cost efficiency and infrastructure impact
- Wrong framework choices increase long-term costs through heavy bundles or poor optimization
- Higher hosting expenses and more developer hours spent on fixes
- Leaner frameworks and meta-frameworks designed for performance reduce infrastructure needs
- Teams can focus on innovation rather than firefighting
Time-to-market and developer productivity
- Enterprises in fast-moving markets need teams to deliver features quickly
- Framework with gentle learning curve, strong tooling, and robust ecosystem cuts onboarding time
- Vue is known for its developer-friendly learning path, shortening ramp-up time for new teams
- Speeds up development cycles significantly
Framework choice shapes scalability, performance, costs, and the speed at which new ideas reach customers. For enterprises balancing digital transformation goals, this decision is a strategic lever, not a side note.
Understanding Front-End Framework : Evolution and Impact
Before comparing frameworks, it’s important to clarify what they actually are and how they’ve evolved. This context helps decision-makers understand not only the technical landscape but also why these tools matter for long-term business outcomes.
What a front-end framework is vs a library
A front-end framework is a structured set of tools, rules, and components that developers use to build user interfaces and manage application logic. It provides opinionated patterns for how code should be organized, tested, and deployed. In contrast, a library like React on its own offers reusable pieces of code but leaves many architectural decisions to the development team. This difference matters for enterprises: frameworks create consistency across teams, while libraries offer flexibility at the cost of governance.
The evolution of frameworks
The story of front-end framework development shows why frameworks are so critical today:
- jQuery era: Quick fixes for cross-browser issues, but messy and hard to scale.
- Angular: Introduced structure and a complete toolset for building full applications. Popular with enterprises needing large-scale apps.
- React and Vue: Brought component-driven design and flexibility. Developers gained efficiency, but with more freedom came more choices.
- Modern meta-frameworks: Tools like Next.js, Nuxt, and SvelteKit build on React and Vue, adding server-side rendering, static generation, and performance optimization out of the box. These frameworks directly address modern needs such as SEO, Core Web Vitals, and edge deployment.
Why this matters for enterprises
The evolution shows a clear pattern:
- Frameworks moved from solving developer pain points to enabling business outcomes
- jQuery solved browser headaches → Angular brought enterprise stability → React/Vue improved developer productivity → Meta-frameworks now tackle SEO and performance optimization
- For enterprises: framework choice today aligns with how the web itself is evolving
- It’s not just about features – it’s about staying competitive in digital transformation
React vs Vue vs Angular : Front-End Framework Comparisons for Headless Commerce
Below, we compare React, Vue, and Angular in the context of headless commerce. We highlight strengths, trade-offs, and real outcomes from companies that have implemented them. This comparison helps show what each framework delivers in practice for businesses concerned about performance, scalability, and SEO.
1. React
Strengths
- Very flexible; large ecosystem of tools and libraries.
- Excellent for headless commerce stacks (React + Next.js or React + Hydrogen).
- Strong support for server-side rendering (SSR), static generation, and incremental static regeneration, which help with SEO and page load times.
Weaknesses
- Because React is often used with many auxiliary tools (state management, routing, form handling), complexity can creep in. Requires good architecture discipline.
- Bundle sizes can become large if not optimized, which can degrade performance on mobile or low bandwidth connections.
Real-World Case Study: Saranoni using Shopify Hydrogen
- Business challenge: Saranoni’s website using standard Shopify theme and many apps had very slow page load times (5-20 seconds) especially for product pages, causing poor user experience and low conversions.
- Framework approach: Moved to a Hydrogen based headless approach using Pack + Shopify + React/Hydrogen, eliminated many unnecessary apps, optimized content loading.
- Outcomes: Page load times dropped to between 1-2 seconds for most pages; conversion rates rose by ~33%; reduction in number of server requests; easier maintenance and design flexibility.
Real-World Case: Half Helix / Shopify Supply
- Challenge: Shopify’s supply store needed a fast, reliable storefront to support large traffic (launch day, promotional campaigns) with high performance metrics out of the box.
- Approach & Outcome: The Hydrogen built site achieved Google Lighthouse scores in the high 90s on launch; high performance on mobile; almost 99% increase in new user sessions on promotional day; minimal performance issues despite heavy traffic.
2. Vue
Strengths
- Easier to onboard; generally fewer moving parts at start for small to mid-size teams.
- Next.js adds SSR, static generation, and good performance optimizations out of the box.
- Works well for interactive UI elements, content-heavy pages, and features like filters, category browsing, where page interactivity is needed.
Weaknesses
- Enterprise-scale integration and global support can lag behind React. Some third-party tools or large enterprise ecosystems are more “React first.”
- Performance pitfalls possible if applications depend heavily on many dynamic components without proper lazy loading or code splitting.
Real-World Case: Alibaba’s SSR / Vue Usage
- Business challenge: During the Double 11 (Singles Day) shopping festival, Alibaba needed its “virtual venue” pages to open in under a second for user engagement, across a wide range of devices including low end Android phones.
- Approach: Adopted server-side rendering for its virtual venue; combination of frontend and backend optimization; use cached module loading and rendering logic moved to server side.
- Outcomes: The “one-second opening rate” (percentage of visitors who see content within one second) rose to ~82.6%; Android devices saw over 100% improvement in visible rendering time; click-through rate (CTR) on core pages increased by up to ~5%.
Additional Vue Example.
Trivago using Vue to improve real-time filters and search experience; users see faster responses when browsing and filtering; better UI interactivity.
3. Angular
Strengths
- Built for structure: TypeScript by default, well-defined patterns, strong for large-scale apps with multiple teams.
- Good built-in tooling for routing, forms, modularization.
- Long history in enterprise. Teams value stability, maintainability, and mature support.
Weaknesses
- Bundle size tends to be heavier; initial load may suffer if not carefully optimized.
- Steeper learning curve for developers new to Angular; productivity may lag during onboarding.
Real-World Case Study: This Dot Labs with Angular
- Business challenge: A financial services platform with high user volume (nearly two million daily users) had SEO ranking risks due to poor performance metrics on its Angular site. Metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and Time to Interactive (TTI) were causing search engine penalties.
- Approach: Detailed performance analysis, identified major bottlenecks (rendering, large unused JS, non-optimized images), implemented optimizations: lazy loading, code splitting, image optimizations, server side resources cached, asset compression etc.
- Outcomes: Improved SEO ranking; better Core Web Vitals metrics; reduced bounce rate; improved user experience particularly on slower devices. (Exact improvements depend on project but the test showed measurable positive lift in SEO visibility).
4. Comparison Summary Table
Below is a summary comparing the three frameworks in headless commerce contexts, based on real business outcomes and trade-offs:
| Dimension | React (with Hydrogen / Next.js) | Vue (with Nuxt) | Angular |
| Initial Load Time & SEO | Very strong when SSR / Hydrogen used; e.g., Saranoni: 1-2s load time; Allbirds etc saw big CWV improvements. | Strong for interactive and content heavy sites; Alibaba’s SSR improved visible load and CTR. | Good after optimizations; but initial load can be slower; needs careful bundling and lazy loading, as in financial client case. |
| Flexibility & Ecosystem | Very large; many plugins, headless commerce integrations; Hydrogen, Next.js etc. | Good ecosystem, especially for content-heavy sites, Vue Storefront etc. | More opinionated; fewer headless commerce examples but strong in enterprise internal tools and regulated environments. |
| Developer Onboarding / Productivity | Higher cost to start (learning React + headless + SSR) but high payoff; teams get faster iteration after initial setup. | Lower entry barrier; quicker productivity for small to medium teams. | Steep learning; requires discipline, but once patterns are established, maintenance tends to be stable. |
| Scalability & Maintenance | Scales well especially with componentization, micro frontends, edge deployment. | Scales well for content platforms, marketplaces; works well if modules are kept clean. | High scalability for large enterprise systems with many modules; TypeScript and strong patterns help avoid drift. |
These real examples show that there is no “one size fits all.” React with Hydrogen shines for headless commerce and performance optimization; Vue is strong for sites needing fast interactivity and good content handling; Angular remains a solid choice when enterprise structure, maintainability, and long-term support are critical.
Front-End Framework Performance Optimization: React vs Vue vs Angular
Performance optimization is one of the most critical factors in framework choice. For enterprises, it is not just a technical metric but a driver of business outcomes: faster sites rank higher on search engines, convert better, and reduce infrastructure costs. Each of the three leading frameworks – React, Vue, and Angular – has a different profile when it comes to optimization.
Key Metrics That Matter
- Core Web Vitals (CWV): Google’s metrics around Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
- Bundle Size: How large the JavaScript payload is, which impacts initial load times.
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR): How efficiently a framework supports rendering content on the server for SEO and faster perceived performance.
- Lazy Loading and Code Splitting: Techniques to load only what users need, improving interaction speed.
React and Next.js
React on its own is client-side focused, which can hurt SEO and initial load performance. Paired with Next.js or Hydrogen, it becomes a strong performer. Companies like Saranoni cut page load times from 5–20 seconds to 1–2 seconds using Hydrogen, resulting in higher conversion rates. Another example is Allbirds, which migrated to a headless React and Next.js architecture and saw measurable improvements in Core Web Vitals, boosting both SEO rankings and customer engagement.
Vue and Next.js
Vue shines when paired with Nuxt.js. Server-side rendering comes built-in, making performance optimization easier. Alibaba, during its Singles Day festival, implemented Vue with SSR and saw a one-second visible rendering rate for over 80% of users, including those on low-end Android devices. That translated into better user engagement and higher click-through rates, proving that Vue with Nuxt can deliver results at global scale.
Angular
Angular includes many tools out of the box, but this can lead to heavier bundles. Without optimization, applications may suffer from slower initial loads. However, enterprises that tune Angular see strong results. In one financial services case, performance analysis identified heavy JavaScript and inefficient rendering as bottlenecks. After implementing lazy loading, code splitting, and image optimizations, the platform improved Core Web Vitals scores, which directly improved SEO visibility and reduced bounce rates.
Business Impact
- Faster load times improve search rankings and reduce customer drop-off.
- Optimized frameworks lower hosting costs by reducing unnecessary server strain.
- Teams spend less time fixing performance issues and more time building features.
For enterprises running headless commerce or global applications, performance optimization is not optional. Frameworks that support SSR, efficient bundling, and edge delivery like React with Next.js or Vue with Nuxt – tend to lead the pack. Angular, while heavier, remains viable when paired with disciplined performance tuning and is often favored for stability in enterprise-scale environments.
Developer Experience and Ecosystem Support in Front-End Framework
Performance and scalability may drive the headlines, but developer experience often determines whether a project succeeds in the long run. A framework that feels intuitive, has strong tooling, and connects easily with the platforms an enterprise depends on will save months of effort and reduce frustration for teams.
Learning curve and onboarding
React has become the most widely adopted option, which means most developers are familiar with it. That reduces hiring risk and shortens onboarding. At the same time, React requires choices about state management, routing, and other essentials, which can slow teams down if not guided by experienced architects.
Vue is often praised for its gentle learning curve. Many teams find they can get productive in days rather than weeks, which is valuable for companies with smaller engineering groups or faster product cycles.
Angular has the steepest learning curve of the three. It is highly structured and TypeScript-driven, which means new developers may take longer to ramp up. The payoff is consistency across teams, which can be crucial in large enterprises managing many applications.
Real-world scenario: Enterprise SaaS choosing Angular for stability vs React for flexibility
We recently worked with an enterprise SaaS company serving Fortune 500 clients in healthcare and finance. As they scaled from 50 to 500 employees, they needed to rebuild their platform architecture. The leadership team faced a common dilemma: React offered faster development cycles and easier talent acquisition, but Angular provided the structure and governance their regulated environment demanded.
In our consulting experience, this decision often comes down to three factors:
- Compliance requirements: Healthcare and financial clients need audit trails, consistent patterns, and predictable code structure—Angular’s strengths
- Speed to market: Competitive pressure demands rapid feature delivery, where React’s flexibility and ecosystem shine
- Team scalability: With multiple development teams across regions, Angular’s opinionated structure prevents architectural drift
The right choice isn’t about which framework is “better”—it’s about which one accelerates your specific business goals while managing risk. RBM helps enterprises weigh these trade-offs by connecting technical capabilities to measurable outcomes like time-to-market, compliance costs, and developer productivity.
Ecosystem and integrations
Framework choice also affects how easily you can integrate with headless CMS, commerce engines, or enterprise APIs. React dominates in this area. Tools like Next.js, Hydrogen, and Gatsby make React the default for many headless commerce projects, with plug-and-play integrations for Shopify, Contentful, and CommerceTools.
Vue is growing its enterprise ecosystem, with Nuxt powering SEO-friendly sites and Vue Storefront supporting commerce integrations. It is strong for content-heavy and marketplace applications.
Angular, while less common in headless commerce, remains a mainstay in financial services, telecom, and government, where robust structure and long-term maintainability outweigh ecosystem flexibility.
Community and Longevity: Which Front-End Framework is Future Proof?
Community adoption and hiring trends
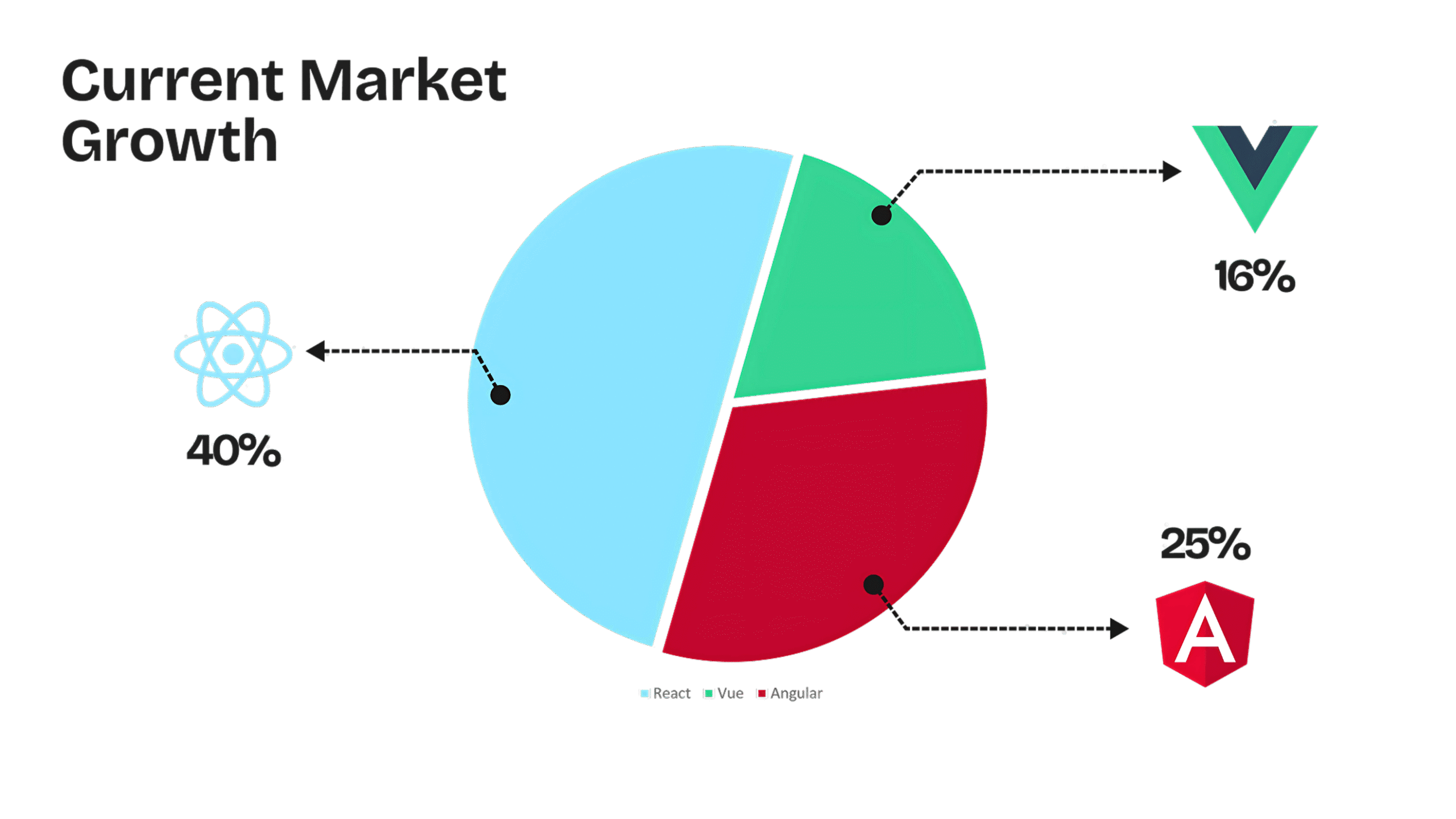
A framework with a big, active community makes hiring easier and reduces project risk. React has the largest developer pool and shows up in job listings across regions. The State of JavaScript 2024 survey confirms this trend, with React maintaining its dominant position while Vue holds steady as the second most popular choice among 40,000+ developers worldwide. That means shorter time to hire and more contractors available when you need burst capacity.
Vue has strong pockets of adoption, especially in parts of Europe and Asia, which can be an advantage if your business operates there. Angular remains common in large enterprises and government projects, so if you need experienced engineers who know strict patterns and TypeScript you will find them in those markets.
Open source activity (GitHub, npm downloads)
Look beyond star counts and watch the rhythm of commits, issue responses, and package downloads. Regular releases, prompt security fixes, and active maintainers signal a healthy project. A broad ecosystem of plugins and official tools also matters because it reduces the need for custom work. Healthy open source activity means fewer surprises when a dependency needs an update or when you must troubleshoot production issues.
Long term stability and risks
Consider who backs the project and how decisions are governed. Frameworks with corporate sponsorship and a clear roadmap lower the chance of sudden abandonment. But even popular projects carry migration risk when major versions change. For enterprises that must minimize risk, plan for abstraction and incremental upgrades. Use modular architecture so a future migration is limited to a few components rather than the whole application.
Practical checklist for evaluation:-
• Check hiring trends in your core regions
• Review GitHub activity and release cadence for the last year
• Confirm major companies using the framework in production
• Assess migration cost and create an upgrade plan
These checks help you judge not just how a framework performs today but how safe it is as a foundation for the next five years
Beyond the Big Three: Emerging Players
While React, Vue, and Angular dominate most enterprise decisions today, a new generation of frameworks is quietly shaping what the future of front-end framework development could look like. These emerging players are designed to push the limits of performance, developer productivity, and edge delivery.
Svelte and SvelteKit: compile-time efficiency
Unlike traditional frameworks that ship a runtime, Svelte compiles components at build time, resulting in smaller bundles and faster load speeds. SvelteKit extends this with routing, server-side rendering, and static site generation. For enterprises, this means leaner applications and improved Core Web Vitals, though the ecosystem is still maturing compared to React or Vue.
Solid.js: fine-grained reactivity
Solid.js takes a different approach to reactivity, updating only the parts of the DOM that change. This delivers performance close to hand-written JavaScript. The framework has a growing community and strong benchmarks, but adoption is still limited, which may concern enterprises that depend on long-term ecosystem stability.
Qwik: resumability and edge-first design
Qwik introduces the concept of resumability, which allows applications to start instantly by loading only what is needed and resuming state at the edge. This model is well-suited for global applications where latency is a concern. Enterprises with heavy international traffic will want to watch how Qwik evolves, especially as edge computing becomes mainstream.
Why enterprises should track but not rush adoption
These frameworks bring exciting innovation, but they are still in early stages. JavaScript Rising Stars 2024 tracking confirms this assessment, showing that while frameworks like Svelte and Solid.js are gaining GitHub stars rapidly, their enterprise adoption remains limited compared to the established trio. For most enterprises, the risks around hiring, support, and ecosystem maturity outweigh the benefits today. The pragmatic approach is to track these tools, run pilot projects, and be ready to adopt once they stabilize and show wider adoption.
Practical Case Studies: Real Companies Choosing Frameworks
Framework decisions are not abstract. Real companies have adopted React, Vue, and Angular at scale, and their results show how the right choice can impact business performance.
Shopify Hydrogen (React)
Shopify introduced Hydrogen, a React-based framework, to help merchants build faster, more flexible headless storefronts. Early adopters saw dramatic improvements in page load speeds, which translated into better Core Web Vitals and higher search rankings. For global brands running on Shopify, Hydrogen meant scalability without compromising SEO.
Splits59 (React + Next.js)
Activewear brand Splits59 rebuilt its storefront using React and Next.js. The change improved Core Web Vitals, reduced bounce rates, and gave marketing teams more editorial flexibility through a headless CMS. Faster load times not only improved user experience but also lifted conversion rates, demonstrating how React with Next.js can balance performance and content agility.
Alibaba and Xiaomi (Vue)
Alibaba leveraged Vue to handle the massive traffic spikes of its Singles Day shopping festival. With server-side rendering in place, pages loaded quickly even on lower-end devices, creating a seamless experience for millions of users worldwide. Similarly, Xiaomi used Vue to support localization across multiple markets, ensuring fast load times and consistent performance for international audiences.
Google Ads and Deutsche Bank (Angular)
Google Ads itself runs on Angular, which underscores its strength for large, complex applications. Angular’s opinionated structure and TypeScript foundation allow teams to maintain consistency across massive codebases. Deutsche Bank also adopted Angular for internal platforms where governance, reliability, and long-term maintainability were essential. In both cases, Angular delivered stability in highly demanding environments.
Key lessons learned
React excels when flexibility, ecosystem integrations, and SEO-driven performance are top priorities. Vue demonstrates its strength in commerce and global-scale use cases where speed and localization are critical. Angular proves its value in highly regulated or complex enterprise platforms where governance and predictability matter most.
For enterprises, these case studies highlight the real-world trade-offs. The best framework is not the one that trends on GitHub but the one that aligns with business strategy, user expectations, and long-term scalability goals.
Decision Framework: How to Choose for Your Business
With so many options available, the most practical way to approach framework selection is to evaluate it against clear business goals. Rather than chasing popularity, enterprises should use a structured decision process.
Checklist for evaluation
- Scalability: Will the framework support growth across multiple teams, products, and geographies?
- SEO performance: Does it handle server-side rendering and Core Web Vitals effectively?
- Cost efficiency: How do bundle size and infrastructure needs affect hosting and maintenance costs?
- Developer availability: Can you easily hire and onboard talent skilled in the framework?
- Integrations: Does the framework connect smoothly with your headless CMS, commerce engine, or enterprise APIs?
Mapping frameworks to business goals
- React: Best fit when flexibility, ecosystem integrations, and SEO performance are top priorities. Works well for enterprises adopting headless commerce and rapid innovation cycles.
- Vue: Strong choice for global commerce and content-heavy platforms where speed, localization, and developer productivity matter.
- Angular: Most effective for large, regulated, or complex environments where governance, predictability, and long-term stability outweigh speed of experimentation.
RBM’s role in guiding the decision
Framework choice is not one-size-fits-all. At RBM, we partner with enterprises to weigh technical trade-offs against business strategy. Our consulting approach helps CIOs, CTOs, and product leaders align framework decisions with transformation goals balancing performance, scalability, and time-to-market. Whether building a commerce storefront, a SaaS platform, or an enterprise portal, RBM ensures the chosen framework accelerates growth rather than creating roadblocks.
Tech Trends Shaping the Future
The front-end framework ecosystem is evolving rapidly, and enterprises need to plan for technologies that will define the next three to five years. Framework choice today should anticipate these shifts, not just solve immediate needs.
Server-side rendering and edge computing
Frameworks that support server-side rendering and edge delivery are becoming essential. By rendering closer to the user, companies can achieve faster load times and more reliable global performance. React with Next.js, Vue with Nuxt, and even emerging frameworks like Qwik are positioning themselves for this edge-first world.
Jamstack and headless CMS
Decoupled architectures are now mainstream. Jamstack combined with headless CMS platforms gives enterprises the flexibility to update content without relying on engineering teams, while frameworks handle rendering and performance. This trend reduces time-to-market and empowers marketing and editorial teams with greater autonomy.
AI-assisted development
AI is beginning to influence how developers build applications. From code generation to performance optimization, AI-powered tools are speeding up workflows and reducing repetitive tasks. Framework ecosystems that integrate with AI-driven productivity tools will make teams more efficient and help enterprises deliver features faster.
Implications for planning 3–5 years ahead
Enterprises should view framework decisions as part of a broader digital strategy. The frameworks most likely to stay relevant are those that embrace server-side rendering, edge-first performance, and integration with headless and AI-driven workflows. Planning ahead means not only choosing the right framework today but also preparing teams and architectures to adapt as these trends become industry standards.
Conclusion
There is no single framework that fits every business. React, Vue, and Angular each bring their own strengths to the table. React offers flexibility and the richest ecosystem, Vue provides simplicity and fast adoption, and Angular delivers structure and stability for complex enterprise environments.
The right choice depends on your context. Teams focused on rapid innovation and headless commerce integrations often lean toward React. Businesses that value a lighter framework with strong performance out of the box may find Vue compelling. Highly regulated industries or companies running large, complex platforms often prefer Angular for its discipline and predictability.
Looking ahead, enterprises should think about more than popularity. Future-proofing means considering community strength, ecosystem growth, SEO support, and how well the framework aligns with digital transformation goals. These factors will determine whether your platform can scale, stay performant, and remain cost efficient over the long term.
At RBM, we work with enterprises to match the right framework to the right business challenge. Our experience in product engineering, commerce solutions, and enterprise search allows us to guide teams through these decisions with a balance of technical depth and business strategy. With the right framework in place, enterprises can accelerate time to market, optimize performance, and unlock the full value of digital transformation.














