Quick Summary:
- Machine learning in ecommerce improves how decisions are made in real time across pricing, inventory, personalization, fraud, and fulfillment.
- The strongest ecommerce machine learning use cases focus on specific decision gaps such as conversion loss, demand imbalance, fraud risk, and rising cost to serve.
- Retailers use ML in ecommerce to increase conversion rates, improve inventory efficiency, reduce operational costs, and manage risk across high-volume transactions.
- The biggest challenges with ecommerce ML are fragmented data, unclear ownership of decisions, model drift, and scaling beyond isolated pilots.
- Successful machine learning for ecommerce connects models directly to storefronts, checkout, pricing, inventory, and support systems where decisions occur.
- Continuous monitoring, feedback loops, and retraining are essential to keep machine learning outcomes aligned with changing customer behavior and demand.
Machine learning in ecommerce can turn a plain website into a smart store that thinks on its feet. 71% of consumers expect personalized interactions, and 76% become frustrated when that does not happen. Yet most ecommerce stores run on batch reports for which the rules were set in the last quarter. By the time teams get a pulse on demand, the revenue is already gone.
Machine learning in ecommerce helps close this gap in real-time. One click on a pair of boots triggers upsell for matching gear. Search results modify as per the shopper’s brand preferences. And every interaction on the web store makes the next one smarter.
Leading companies treat ML in ecommerce as an operating layer. It helps them automatically turn customer signals into revenue decisions. In this article, we’ll go through the most impactful use cases of ML in ecommerce along with the real-world examples.
Top 12 Use Cases of Machine Learning in Ecommerce
Machine learning in ecommerce solves the decision-making gaps that stall growth. Most stores have plenty of data but lack the speed to act on it. Ecommerce machine learning replaces slow, manual guesses with instant, automated actions that increase revenue and lower risk.
These twelve use cases show where the technology builds a real edge. Each example proves how machine learning for ecommerce creates a measurable win for the business.
1. Personalized Product Recommendations
Relevant Suggestion Becomes Tricky at Scale
As product catalogs expand and traffic goes up, maintaining relevance becomes increasingly difficult. And when you serve customers the same recommendations irrespective of intent and preferences, the conversion rates are bound to take a dip. Fixed merchandising regulations can’t keep up with behavioral shifts and tend to drive teams to greater discounts for market capture.
Machine Learning-Driven Predictive Behavioral Mapping
Machine learning uses browsing patterns, purchase history and product correlations to forecast the next most likely purchase. These forecasts get continuously updated across touchpoints (homepage, product page, post purchase follow-up, etc.) to ensure relevance scales along with the catalog.
Use of ML for Automated Discovery and Cross-Sell Efficiency
Amazon has claimed that its recommendation systems impact a big part of overall sales by enhancing product discovery and cross-sell efficiency. Similarly, other large retailers who deployed comparable ML strategies reported consistent improvements in conversion rates and average order value.
2. Semantic Product Search and Visual Search.
Poor Search Experiences Hurt Sales
Traditional product search breaks down when customers don’t use exact keywords. Shoppers often use vague descriptions, natural language phrases, and even try images to find what they need. The usual rigid keyword-based taxonomies don’t do well in such situations. And it leads to zero-result pages, irrelevant listings, and dead-end experiences.
How ML enables Semantic and Visual Recognition
Ecommerce machine learning uses natural language processing and computer vision to understand meaning rather than keywords. It leverages attributes, contexts, and similarity to match search queries and enhance relevance in both text and visual search experiences.
Use of ML for Intent-Based Discovery and Reduced Search Abandonment
eBay uses a massive similarity engine to help users find items among billions of listings by understanding their intent. Other ecommerce businesses using similar engines report far fewer shoppers leaving the site in frustration. This is especially true on mobile, where customers prefer taking photos or using descriptive words rather than typing exact product names.
3. Dynamic Pricing Optimization
Static Pricing Leaves Revenue on the Table
When the market is volatile and the prices shift now and then, static pricing becomes a liability. Manual updates are slow and always lag behind the market conditions. It either leads to missed revenue opportunities during high-demand or unnecessary margin erosion because of ill-timed discounts.
Demand-Aware Pricing Through Machine Learning for Ecommerce
ML-based pricing engines factor in demand trends, competition, and past price elasticity. It makes sure recommendations get updated within set guardrails to safeguard margins, brand positioning, and regulatory needs.
Use of ML for Margin Protection and AOV Growth
A luxury furniture retailer improved pricing decisions using demand-aware pricing intelligence delivered through RBMsoft. We built a recommendation engine that analyzed historical transaction data, demand patterns, and competitive price movements to generate dynamic price recommendations for each product. The engine also automatically accounted for margin floors, brand positioning, and promotional boundaries.
As a result, fixed-price margin leakage was reduced, close rates on high-value products improved, and average order value increased without expanding discounting.
Ready to stop manual price updates?
Eliminate margin leakage and automate your pricing guardrails with RBMsoft
Consult our experts4. Predictive Inventory and Demand Forecasting
Demand Signals are Often Missed
Ecommerce companies find it difficult to strike a balance between availability and working capital in quickly moving catalogs. The spreadsheet-based forecasting is not reliable in demand volatility across regions, channels, and campaigns. The resultant effect is a high number of stockouts on fast-moving SKUs and a high number of stocks lying dead in low-selling locations.
Multi-Node Forecasting Machine Learning Models for Ecommerce
Predictive models consider the historical sales, customer demand indicators, price adjustments, promotions, and local behavior. SKU and fulfillment-node-level forecasts are created and updated at the continuous level. This allows planning inventory decisions based on current demand patterns as opposed to lagging indicators.
Use of ML to Reduce Carrying Costs
The global retailer Decathlon uses applications of machine learning in ecommerce to match its stock with local buying habits. This strategy ensures products are available during busy seasons while reducing leftover stock in slow areas. As a result, they move inventory faster and spend less on storage without making the supply chain more complicated.

5. Supply Chain and Fulfillment Optimization
Rigid Routing and Operational Constraints
Ecommerce fulfillment breaks down when demand signals are unclear and routing rules stay static. Orders are often shipped from the nearest location without considering capacity or delay risk, leading to late deliveries, higher shipping costs, and inconsistent customer experience during peak demand.
Predictive Routing and Logistics Using Machine Learning for Ecommerce
Machine learning models look at purchase trends and match those against what’s actually happening on the warehouse floor and with your carriers. The system picks out the best way to get a package to a door by weighing speed and cost against the risk of something going wrong in transit. This approach lets the math handle the logistics while you can focus on keeping the inventory from hitting a gap.
Use of ML for Split-Shipment Reduction and Delivery Reliability
Zalando uses this kind of predictive routing to make sure orders go to the fulfillment centers that actually have the room and the staff to handle them. This move cut down on split shipments and helped them stay on schedule even when seasonal demand started to spike.
6. Real-Time Fraud and Anomaly Detection
Breakdown in Transaction Controls
Ecommerce platforms face a persistent risk of payment fraud, account takeover and promotion abuse. Rule-based controls create a high rate of false positives, contribute to slow checkout and inconvenience the honest customer. Simultaneously, late detection magnifies chargebacks, compliance risk and loss of revenue.
Dynamic Risk Scoring Using Machine Learning in Ecommerce
ML modes assess the transactions in real-time based on behavioral cues, device fingerprints, purchase velocities, and past trends. Every transaction gets assigned a dynamic risk score, which responds to changes in fraud tactics. This enables instant decisioning that blocks suspicious activity while preserving a low-friction experience for legitimate customers.
Use of ML for Fraud Prevention and Authorization Optimization
Stripe uses real-time detection on millions of daily transactions to stop fraud without slowing down the checkout. Merchants using these machine learning use cases in ecommerce report fewer chargebacks and more successful payments.
7. Conversational AI for Customer Support
Support Bottlenecks and Scalability Issues
Rising order volumes, increasing delivery inquiries, and growing return requests put enormous pressure on ecommerce support teams. This leads to human agents spend a disproportionate share of their time handling repetitive, low-complexity requests. It not only drives up operational costs but also increases the response time across the board.
Intent Recognition and Agent Assistance with Machine Learning for Ecommerce
The natural language models categorize the intent of the customers and understand chat, email and voice contextually. They trigger automatic replies for usual queries such as order status, refunds and policy queries. For complex cases, agent-assist systems surface relevant customer history, order details, and recommended actions in real time, enabling faster and more accurate resolution. All this without the need for human agents to search info across multiple systems.
Use of ML for Response Time Reduction and Service Consistency
H&M implemented conversational AI on its online platforms to satisfy frequent customer requests. The retailer minimized the average response time and relocated human agents to high-value interactions. This not only minimized the support costs but also elevated the quality of customer support leading to improved uniformity of service quality across markets.
8. Customer Lifetime Value and Churn Prediction
Retention and Value Visibility Gap
The ecommerce teams tend to invest a lot in acquisition without a proper view of the kind of customer that will create long-term value. Marketing expenditures get equitably distributed and the high risk churn is not noticed until the revenue starts reducing. The result of this is inefficient budgeting and loss of retention opportunities.
Value Prediction Through Machine Learning Models for Ecommerce
Predictive models use purchase frequency, order value, browsing and engagement signals to predict future value and churn risk. As customer behavior changes, risk and value scores get continuously recalculated. This gives teams rich and accurate data to put greater emphasis on retention and target incentives depending on anticipated impact.
ML-driven Repeat Purchase Growth and Discount Optimization
Shopify Plus gives its users the advantage of predictive analytics to determine high-value customers and early signs of churn. They implemented the insights generated by ML engines to ensure higher repeat purchase rates and decreased discount dependency. The insights allow them to focus retention programs on customers who are likely to bring about long term revenue.
9. Voice and Multimodal Commerce
Friction in Discovery and Reorder Paths
The traditional search and navigation restrict the ways that customers can search for products and this is more so on mobile and smart devices. Text-only interfaces make the repeat purchase process harder and discovery more difficult in the visually-driven categories. This limits the conversion and repeated participation.
Speech and Vision Processing Using Machine Learning for Ecommerce
ML-powered speech recognition, natural language understanding, and computer vision work together to interpret voice commands, images, and text as unified input signals. They also map customer intent against product catalogs, purchase history, and stated preferences. This allows discovery and reordering through multi-modal interfaces with higher search relevancy.
Use of ML for Frictionless Grocery Reordering
Walmart introduced voice-enabled reordering and image-based search to simplify repeat purchases and grocery shopping. These features minimized the effort required to repurchase items and improved conversion rates.
10. Virtual Try-On and Shoppable AR.
Confidence Gap Before Purchase
Online consumers are reluctant to buy the products that they cannot see, wear, or imagine in real environments. It is this uncertainty that increases the cart abandonment rate and returns, particularly in the fashion, beauty, and home segments. The returns add to the cost of logistics and trim away margins.
Computer Vision and AR Overlays Machine learning models for ecommerce
Computer vision models translate images or camera feeds to extract data around body dimensions, facial features, or spatial measurements of a room. These models then do product overlays on the fly. It allows the customer to eliminate the guesswork and preview the fit, scale, and appearance before buying.
Use of ML to Improve Buyer Confidence
L’Oréal deployed virtual try-on technology across its ecommerce channels to help customers test shades and products digitally. The capability raised confidence in the purchases and reduced the rate of returns and enhanced the participation both on the mobile and web platforms.
11. Real-Time Personalization on the Edge
Delay in Contextual Promotions
Conventional personalization relies on cloud-based processing, introducing latency between customer action and system response. Delayed recommendations reduce their relevance and impact on engagement. At the same time, tightening privacy regulations make centralized collection and processing of granular behavioral data an increasing compliance and reputational risk.
On-Device Relevance Machine learning for ecommerce
ML models deployed on IoT devices process user interactions locally and in real time, generating personalized recommendations and content directly on the device. And because the behavioral data never leaves the device, this architecture delivers both faster response times and stronger privacy compliance by design.
Use of ML for High-Privacy, Low-Latency Engagement
Nike applied edge-based personalization to its mobile applications to provide real-time product and content recommendations. This method improved interaction rates and conversion while maintaining high privacy standards.
12. Artificial Data in Machine Learning Training.
Data Availability Gaps
Building sophisticated ML models in ecommerce requires large volumes of high-quality customer data. Often, such data is sensitive, regulated, and difficult to share across teams or with external partners. You end up in a situation where the data most valuable for model development is often the data least accessible.
Privacy-Safe Datasets Ecommerce machine learning
Generative methods produce artificial data that condense the statistical characteristics of actual transactions and consumer activity without copying any of the recognizable records. Teams can train, validate, and stress-test machine learning models using these datasets while maintaining strict data isolation.
Use of ML for Accelerated Model Development and Risk Modeling
American Express uses artificial data to facilitate fraud detection and risk modeling programs without exposing the cardholder data. The practice has minimized their reliance on live datasets, minimized the time of the model development phase, and enhanced adherence to global data protection principles.
Exploring ML use cases in ecommerce can surely drive lots of positive results for your business. We’ve highlighted a few of those in the next section.
Are you maximizing your data’s potential?
Don’t let your customer data sit idle. Transform your recommendation engine from a guessing tool into a revenue driver
Consult Our ML Strategy TeamBenefits of Machine Learning in Ecommerce
Machine learning in ecommerce sharpens every decision about costs, customer experiences, and risks.
Here are few core benefits with long-term positive impact for your business
Improved Demand Capture to Grow Revenue
Ecommerce businesses keep looking for ways to increase traffic to improve. However, better demand capture can be a bigger goldmine for improving sales. Shoppers land on the website with the intent to buy but don’t find relevant products or discounts and leave.
Ecommerce machine learning helps you detect, predict, and act on buying signals. It does so by analyzing browser history, tracking past purchases, identifying behaviour patterns and so on.
This leads to:
- Increased conversion rate due to better intent identification.
- Increased values of orders as a result of corresponding cross-sell and upsell.
- Quicker product search in the complicated catalogs.
Cost Reduction Through Decision Automation
There’s often a lag between signal and response in ecommerce. Pricing adjustments and inventory corrections happen after compressed margins and stockouts. And this reactive decision-making only increases operational costs for you.
Machine learning shifts these decisions from reactive to proactive. Pricing, inventory levels, and risk assessments get executed automatically based on real-time demand signals, behavioral data, and market conditions. You essentially replace human delays with high-frequency decisions with strategic oversight.
The measurable impact includes:
- Lower return and refund handling costs through better alignment of products to demand
- Reduced fraud losses and chargebacks via transaction-level risk scoring
- Fewer manual interventions across pricing and inventory workflows
Personalization With Control and Consistency
Personalization often fails when an ecommerce business uses fragmented systems to deliver it. Customers encounter different recommendations on the app than on the website. There might also be promotional messaging conflicts across channels
Ecommerce machine learning consolidates personalization into a unified decisioning layer that operates across every customer touchpoint. Customer insights, behavioral signals, and preference data feed a single model that applies consistent logic to product recommendations, content sequencing, and offer targeting
This leads to:
- Consistent experiences across digital and service channels
- Faster adaptation to behavior shifts without constant rule maintenance
- Higher customer lifetime value through more relevant engagement
Operational Efficiency Across the Commerce Stack
Ecommerce operations that depend on periodic review cycles are structurally late to every problem they encounter. By the time an issue surfaces in a scheduled review, it has already impacted the revenue.
Machine learning replaces periodic review with continuous sensing. It monitors data signals across the business in real time to ensure automated detection and escalation of anomalies before they reach the balance sheet.
This improves stability and coordination and leads to:
- Fewer stockouts and overstocks through predictive planning
- Faster detection of fulfillment and transaction issues
- Stronger alignment between merchandising, supply chain, and marketing
Strategic Value Beyond Immediate ROI
The most significant impact of ML in ecommerce extends beyond any individual use case. Each automated decision generates measurable feedback and creates a system that continuously refines itself.
Over time, this transforms your commerce operation from one that executes static strategies into one that learns and adapts as a core operational characteristic.
Key outcomes include:
- Clear governance over automated decisions, reducing operational risk
- Faster experimentation with minimal disruption
- A foundation for AI-driven growth that does not rely on a single platform
ML’s value compounds as data quality improves, models mature, and decision confidence grows, creating a durable competitive advantage.
Challenges of Implementing Machine Learning in Ecommerce
While machine learning in ecommerce gives you a real edge, it is never as simple as just turning it on. If the rollout isn’t handled poorly, you end up with operational headaches and missed chances to make money. Let’s get to know the challenges of machine learning in ecommerce below:
Messy data and broken signals
Models only work if the data going in is clean and shows up on time. When your information is scattered or just plain wrong, you end up with bad inventory guesses and pricing that doesn’t make sense. This hits your bottom line immediately.
Legacy systems that can’t keep up
Many ecommerce sites were built before real-time decisions existed. Trying to plug ecommerce machine learning into these old systems is difficult. You must ensure that your ecommerce infrastructure is set up so as to integrate the ML features with ease.
Compliances and privacy restrictions
You need customer data to improve these models, but strict laws like the EU AI Act and CCPA now limit what you can do. Overlooking privacy guardrails can lead to hefty fines and spoiled reputation.. Dealing with this aspect of ML implementation can be tricky, but you cannot skip it.
Models get stale over time
What customers want today is not what they will want next month. If you are not constantly checking and updating your machine learning models for ecommerce, they start giving outdated suggestions. This leads to pricing mistakes and missing obvious fraud. Old logic is a business liability.
Skill gaps prevent model success
To make this work, you need people who understand both the data and the actual business. Most companies have a big gap in skills that slows everything down. Without the right team, you’ll never get past the “test” phase. It just stalls out.
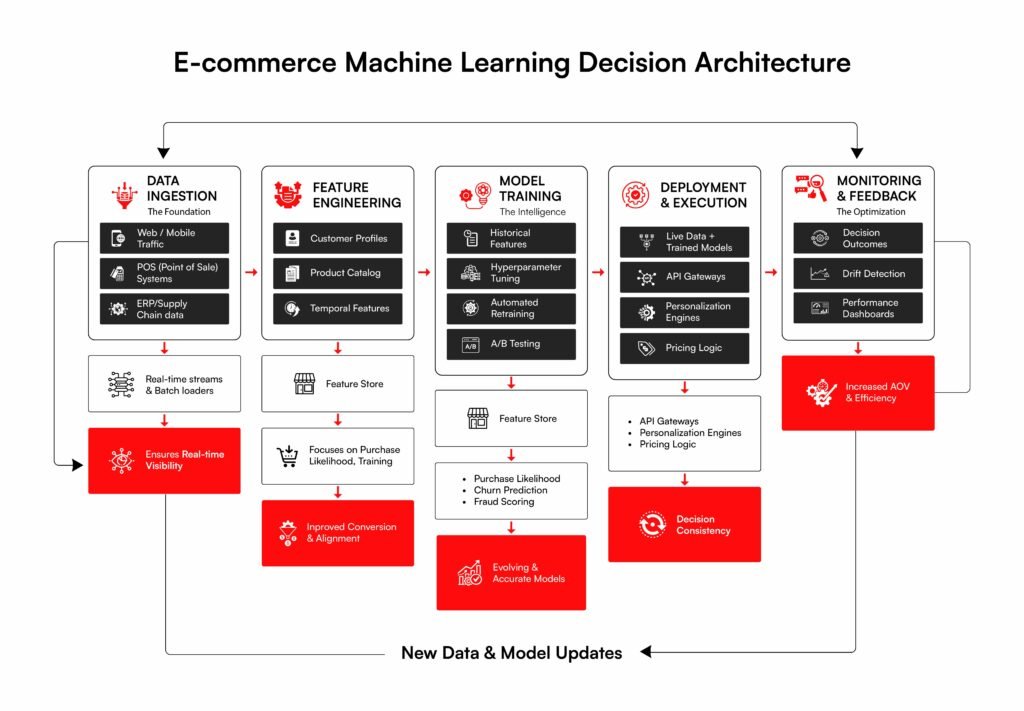
The Decision Architecture Behind Machine Learning in Ecommerce
Ecommerce decisions fail when information arrives too late or differs between channels. Machine learning in ecommerce fixes this by building a direct path that turns raw data into clear, measurable choices.
Data Ingestion
The pipeline begins with continuous data collection from storefronts, mobile applications, warehouse management systems, and transactional platforms. Clean, uninterrupted data flows provide a real-time view of inventory positions, customer behavior, and order activity. Without reliable ingestion, every downstream decision is built on incomplete or outdated information.
Feature Engineering
You take that raw info and turn it into simple signals like how people shop or what prices are doing. These signals help make your choices much more precise so you can actually fix your stock levels and catch fraud before it hits. The quality of these signals directly determines the quality of every decision the system produces.
Model Training
Algorithms learn from what happened yesterday and what is happening now to guess if a visitor will buy or leave. These models require continuous retraining as customer behavior shifts, seasonal patterns evolve, and market conditions change. A model trained on last quarter’s data is making decisions based on outdated assumptions
Deployment and Decision Execution
Trained models feed predictions directly into pricing engines, recommendation systems, and risk scoring tools. These automated choices stay consistent everywhere, which saves you a massive headache and helps the business keep up with the market. This automated execution ensures consistency across channels, provided your ecommerce IT services team has optimized the API layers to prevent latency during high-traffic surges.
Monitoring and Continuous Feedback
You also need to monitor deployed models against business outcomes to ensure that predictions continue to translate into measurable value. Tracking things like order value and fraud helps you tweak the system so it doesn’t just stall out over time. Without this closed-loop monitoring, model performance degrades over time.
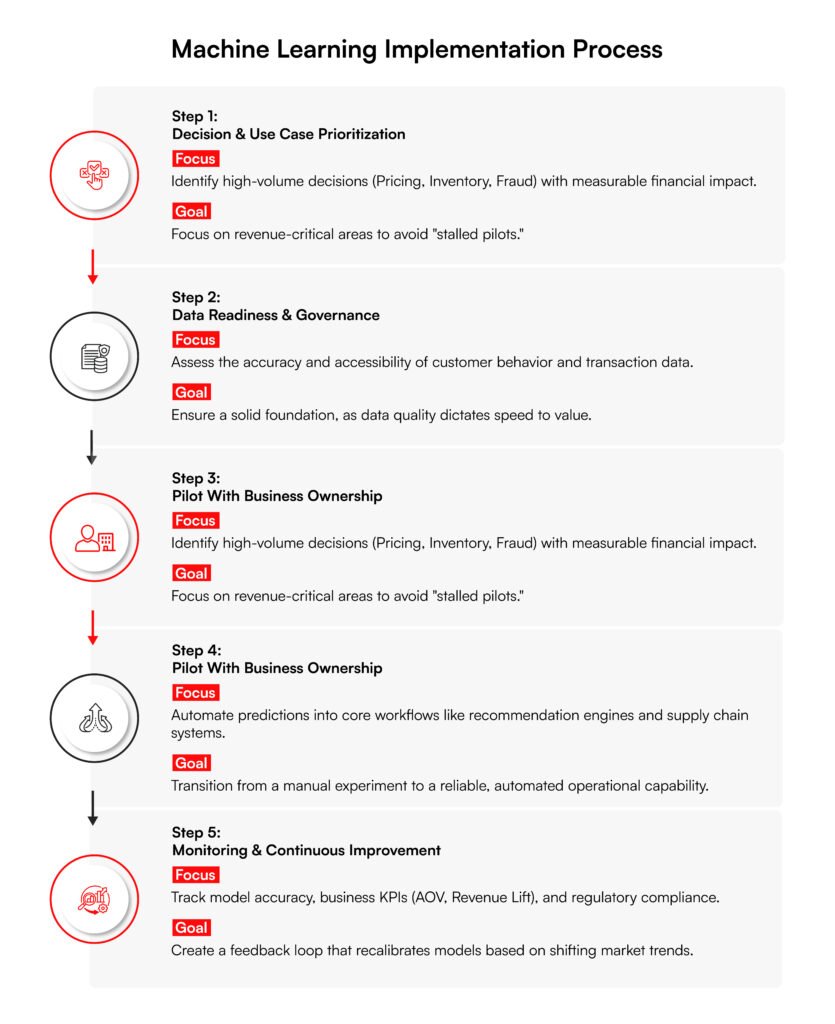
Machine Learning Implementation Process for Ecommerce Businesses
Successful machine learning in ecommerce is not a technology rollout; it’s a fundamental shift in how you make decisions. The following process shows how to cut down on risk, avoid “stalled pilots,” and move from simple experiments to making a real dent in the bottom line.
Step 1: Decision and Use Case Prioritization
Start by identifying the choices that can actually change your revenue or costs. Focus on high-volume decisions like pricing moves, inventory planning, and fraud prevention. Ecommerce machine learning only pays off when applied to actions that happen thousands of times a day and have real financial impact.
- When this works best: High-volume decisions with results you can actually measure.
- When it fails: Big ideas without a single owner or a clear way to track success.
Step 2: Data Readiness and Governance Assessment
Before you start any modeling, you have to see if your data is a mess or actually useful. This includes everything from how customers click to your transaction history and warehouse signals. Weak data quality makes automated choices risky and kills any confidence the team has in the results.
- Key consideration: Your data readiness determines your speed way more than how fancy your model is.
Step 3: Pilot With Business Ownership
Launch a small test tied to one outcome, like a lift in sales or a drop in fraud. You need a business leader who owns the result and knows exactly what success looks like from day one. The whole point of a pilot is to prove the thing works before you try to scale it.
- What to avoid: Running tests in a corner where the people actually running the business don’t have any skin in the game.
Step 4: Scale Through Integration and Automation
Once the math is proven, you have to plug the models into your actual store workflows. Your pricing tools and stock systems should use these predictions automatically without a human getting in the way. Scaling is about making the system reliable so it doesn’t break the business.
- Trade-off to manage: Balancing how fast you can roll things out against keeping the operation stable.
Step 5: Monitoring, Governance, and Continuous Improvement
You need to track both how right the model is and how much money it’s making. Keep an eye on things like revenue lift and cost savings to make sure the system stays on track. Good oversight ensures the decisions are clear and stay in line with what the company is trying to do.
- Long-term outcome: Machine learning for ecommerce becomes a normal part of how you operate instead of a string of projects that eventually stall out.
The Future of Machine Learning in Ecommerce
The next stage of machine learning in ecommerce is about mastering autonomous decision-making across the entire shop. To win in 2026, brands must automate high-frequency tasks while protecting the bottom line. True innovation means building systems that drive growth without running wild.
Agentic systems and autonomous decision flows
Machine learning in ecommerce is shifting toward systems that can plan and fix their own mistakes without constant supervision. For global brands, this requires robust enterprise search solutions that handle pricing, stock, and shipping as one unified move. These systems test different ideas and tweak plans on the fly, turning one-off guesses into a continuous loop of action.
Multimodal product discovery as the default experience
Searching for products won’t be stuck with just typing keywords into a box. People are going to use their voice, photos, and text all at once to show what they actually want to buy. Your platform uses machine learning technology in ecommerce to interpret these mixed signals and deliver precise matches from your catalog. This multimodal approach ends “scroll fatigue” and removes friction for customers tired of hunting through irrelevant results.
Ready to Scale?
Stop managing isolated tools. Build an adaptive ecosystem with RBMsoft to master multimodal search and Agentic AI.
Book Your Free ML AssessmentPrivacy-first and compliant learning approaches
Between the lawyers and the customers, there is a massive push to stop hoarding so much personal info. New ways of doing things, like processing data right on a phone or using fake data sets will let you personalize the site without putting sensitive info at risk. You have to treat privacy like a way to beat the competition rather than just another legal headache to deal with. Trust is going to be the thing that keeps people coming back when everyone else is just trying to scrape their data.
Automation of high-frequency business decisions
As people start to trust ecommerce machine learning results more, the daily grind will shift from manual checks to the machines. High-frequency tasks like changing prices or catching fraud will happen in real time based on what is happening right now, rather than some report from last week. This is one of the key benefits of machine learning in ecommerce: your team can finally stop staring at spreadsheets and start worrying about the bigger picture while the system handles the repetitive stuff.
Conclusion
Machine learning in ecommerce is more than a one-time tech project; it is a core operating discipline. Its value grows when you consistently improve decisions across revenue, cost, and risk. Businesses that treat machine learning for ecommerce as essential infrastructure gain the resilience to adapt as markets and customer behaviors shift.
Those who view ecommerce machine learning as isolated tasks may see small wins, but they miss the long-term advantage of unified decision-making. At RBM Soft, we help brands build machine learning models for ecommerce that function as core capabilities rather than side projects.
Whether you are exploring the benefits of machine learning in ecommerce or need to define a scalable implementation path, our experts are here to help you prioritize high-impact use cases.
FAQs
What are the machine learning compliances and data privacy laws to follow in ecommerce?
Machine learning compliances and data privacy laws in 2026 require strict adherence to the EU AI Act, GDPR, and the Indian DPDP Act. To stay compliant, businesses must implement automated consent management, ensure explainability for automated decisions, and recognize universal opt-out signals like Global Privacy Control (GPC). Prioritizing compliance for implementing Machine learning in ecommerce protects your brand from penalties while building long-term consumer trust.
How can machine learning reduce operating cost and increase revenue?
Machine learning can reduce operating costs and increase revenue by automating high-frequency tasks like dynamic pricing, inventory reordering, and fraud detection. By using ecommerce ml to replace manual spreadsheet reviews, retailers often see a 30% boost in customer retention and a 90% increase in fault detection within logistics. This shift allows teams to focus on strategic AI growth while the system handles repetitive daily execution.
How long does it take to implement machine learning in ecommerce stores?
The Machine learning Implementation Process in ecommerce typically takes between 3 to 9 months, depending on the complexity of the solution. A simple pilot program or a pre-trained recommendation engine can be live in 8 to 12 weeks, while a custom-built, autonomous agentic system that integrates with your ERP and CRM may take 6 months or longer to fully train and deploy.
How much does it cost to implement ai and ml in ecommerce?
Implementing machine learning in ecommerce involves several key cost drivers:
Total Project Scope: Costs range from $20,000 for basic pilot models to over $1 million for enterprise-grade systems.
Mid-Market Average: For mid-sized businesses in 2026, a typical implementation falls between $120,000 and $600,000.
Data Preparation: Cleaning and structuring data is the largest single expense, typically consuming 20–40% of the total budget.
Annual Maintenance: Ongoing support, retraining, and cloud computation require an annual budget of 15–30% of the initial build cost.
What are the most important machine learning use cases in ecommerce?
The most impactful machine learning use cases in ecommerce include personalized product recommendations, demand forecasting, dynamic pricing, and real-time fraud detection. These applications of machine learning in ecommerce allow retailers to improve decision-making across the entire customer journey, significantly boosting conversion rates and reducing operational risk.
How does machine learning improve ecommerce performance in real life?
In real life, machine learning for ecommerce improves performance by aligning product discovery with actual user intent. Retailers use ecommerce machine learning to analyze massive datasets—such as purchase history and browsing patterns—to predict customer needs before they arise. This results in higher revenue efficiency and a more frictionless shopping experience.
Can machine learning reduce operating cost and increase revenue?
Yes, machine learning can reduce operating cost and increase revenue by automating high-frequency decisions like inventory restocking and price adjustments. By using ml in ecommerce to replace manual spreadsheet reviews, businesses minimize human error, reduce stockouts, and capture more sales through automated price optimization.
What are the machine learning compliances and data privacy laws to follow?
Key compliances for implementing machine learning in ecommerce include GDPR, CCPA, and emerging frameworks like the EU AI Act. To maintain trust, businesses must prioritize data privacy by using techniques like federated learning or synthetic data, ensuring they personalize the user experience without compromising sensitive customer information.